This document provides information on Henry's law and its applications. It discusses how Henry's law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas. Raoult's law is introduced as a special case of Henry's law that applies to solutions of volatile liquids. Characteristics of the Henry's law constant KH and examples of applying Henry's law such as carbonation of soft drinks are provided. The document also covers ideal and non-ideal solutions, azeotropes, and colligative properties.

![TOPICS
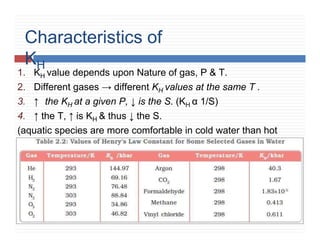
1. Henry’s law [solubility of gas in a liquid].
2. Characteristics of K H .
3. Applications of Henry’s law.
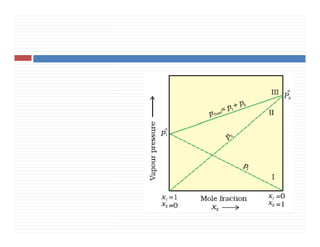
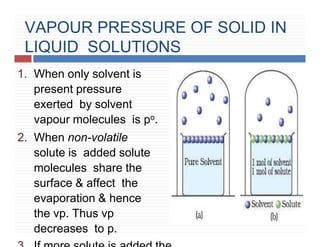
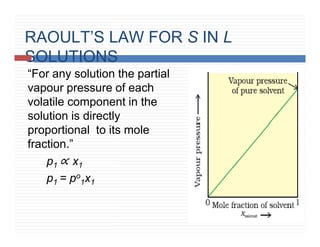
4. Raoult’s law for volatile liquids & for non volatile
solutes.
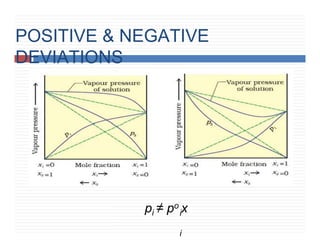
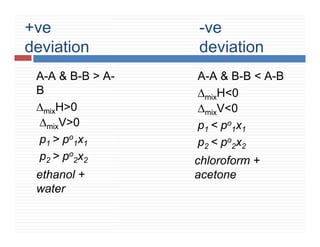
5. Ideal & non ideal solution
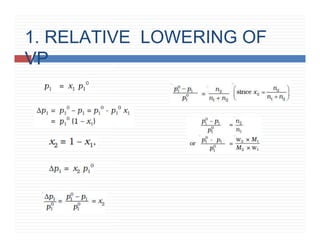
6. Colligative properties – Relative lowering of vapour
pressure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solutionsppt-240328113404-d459783d/85/SOLUTIONS-book-1-unit-1-class-12-ppt-pptx-2-320.jpg)