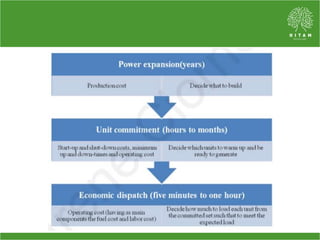
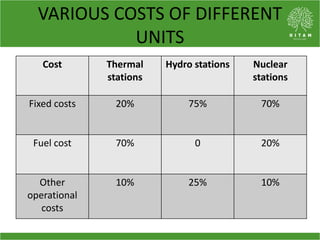
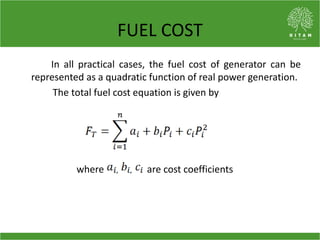
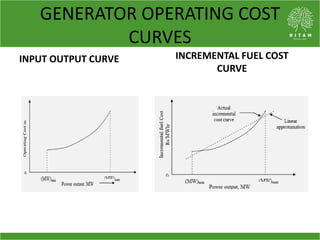
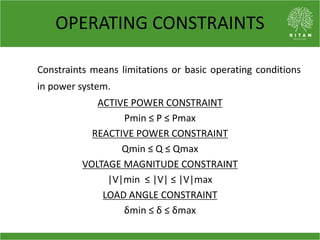
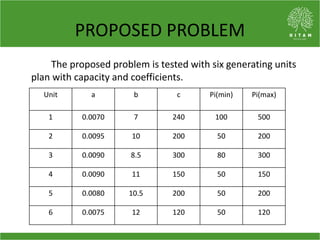
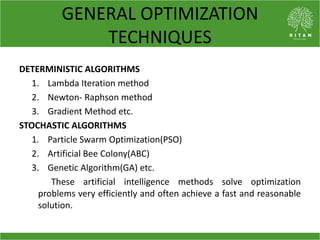
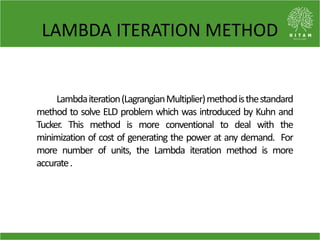
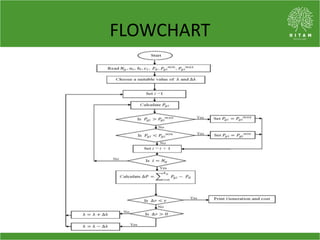
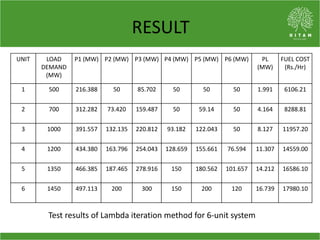
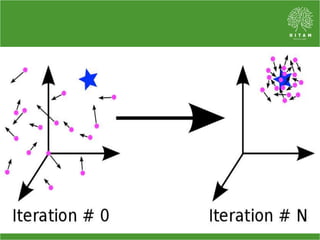
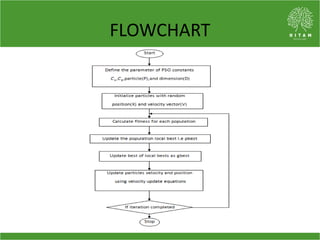
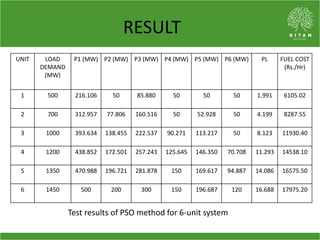
The document discusses the economic load dispatch problem in thermal power stations, aiming to minimize total fuel costs while meeting generation limits and operational constraints. It outlines various techniques, such as lambda iteration and particle swarm optimization (PSO), for solving this optimization problem, highlighting their respective efficiencies and results for a six-unit system. The conclusion notes that while the lambda method relies on initial values, PSO consistently yields converged solutions without such dependencies.