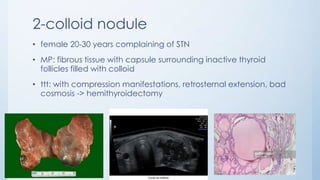
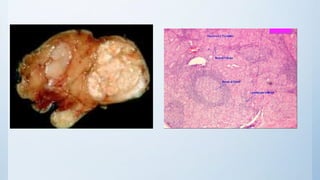
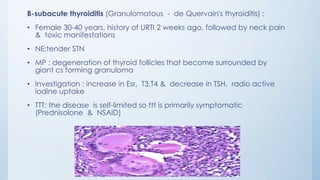
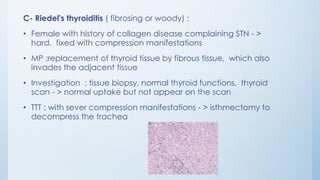
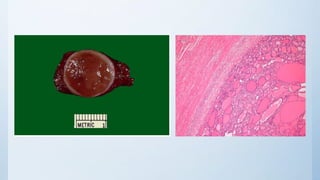
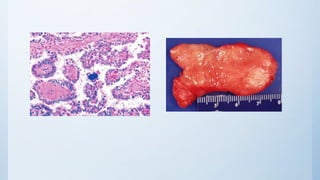
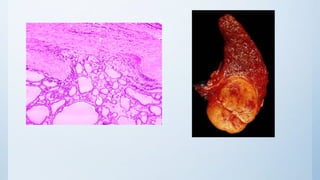
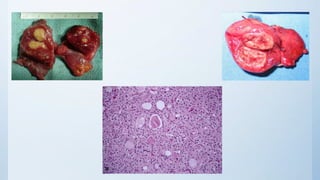
This document summarizes different types of solitary thyroid nodules (STNs), including their clinical presentations, pathological findings, investigations, and treatment approaches. It discusses STNs that may be caused by multinodular goiter, colloid nodules, cysts, autonomous toxic nodules, various forms of thyroiditis, follicular adenomas, and malignant lesions such as papillary carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, and medullary carcinoma. For each condition, it provides details on symptoms, microscopic pathology, diagnostic testing, and surgical or medical management strategies.