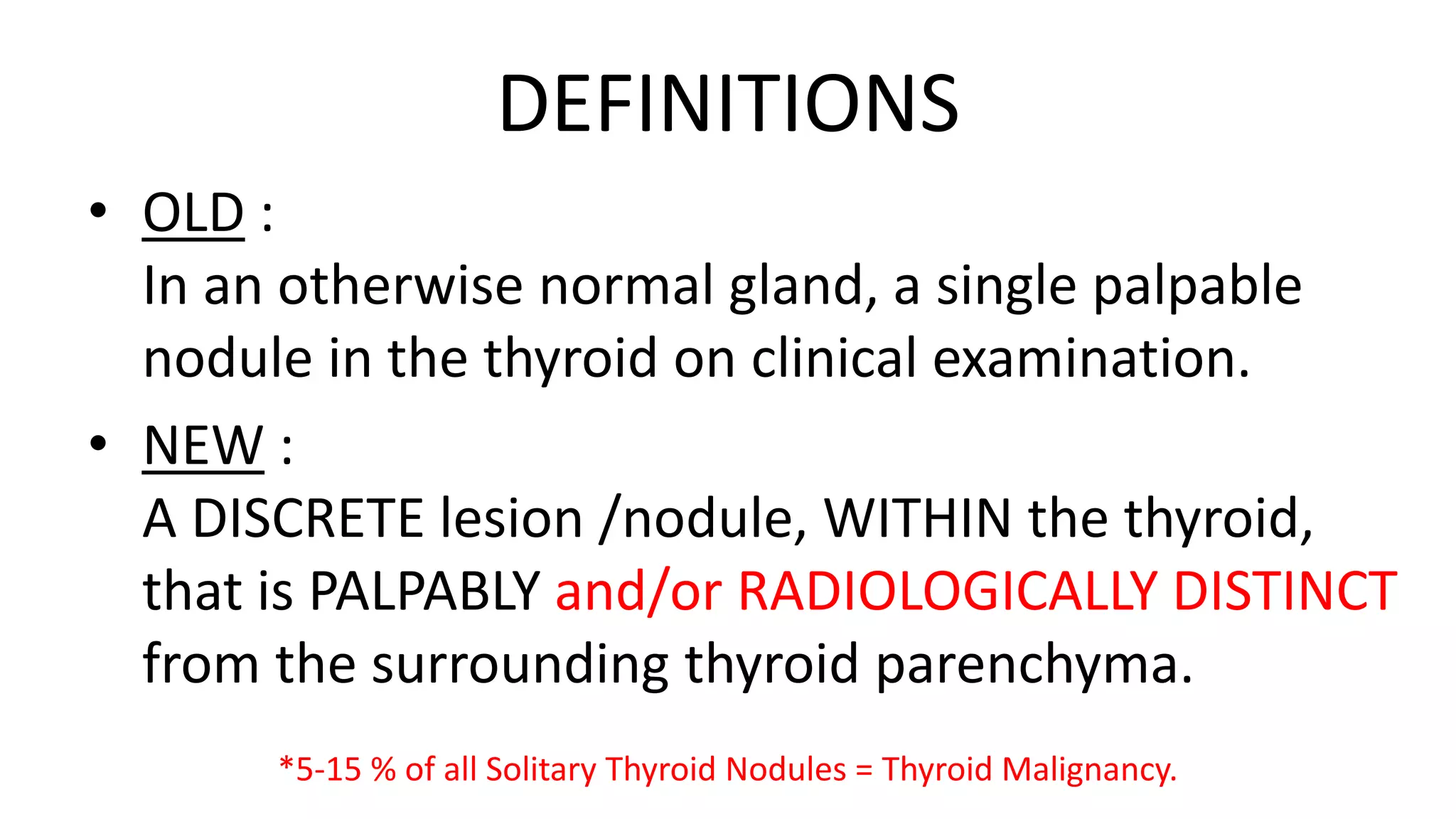
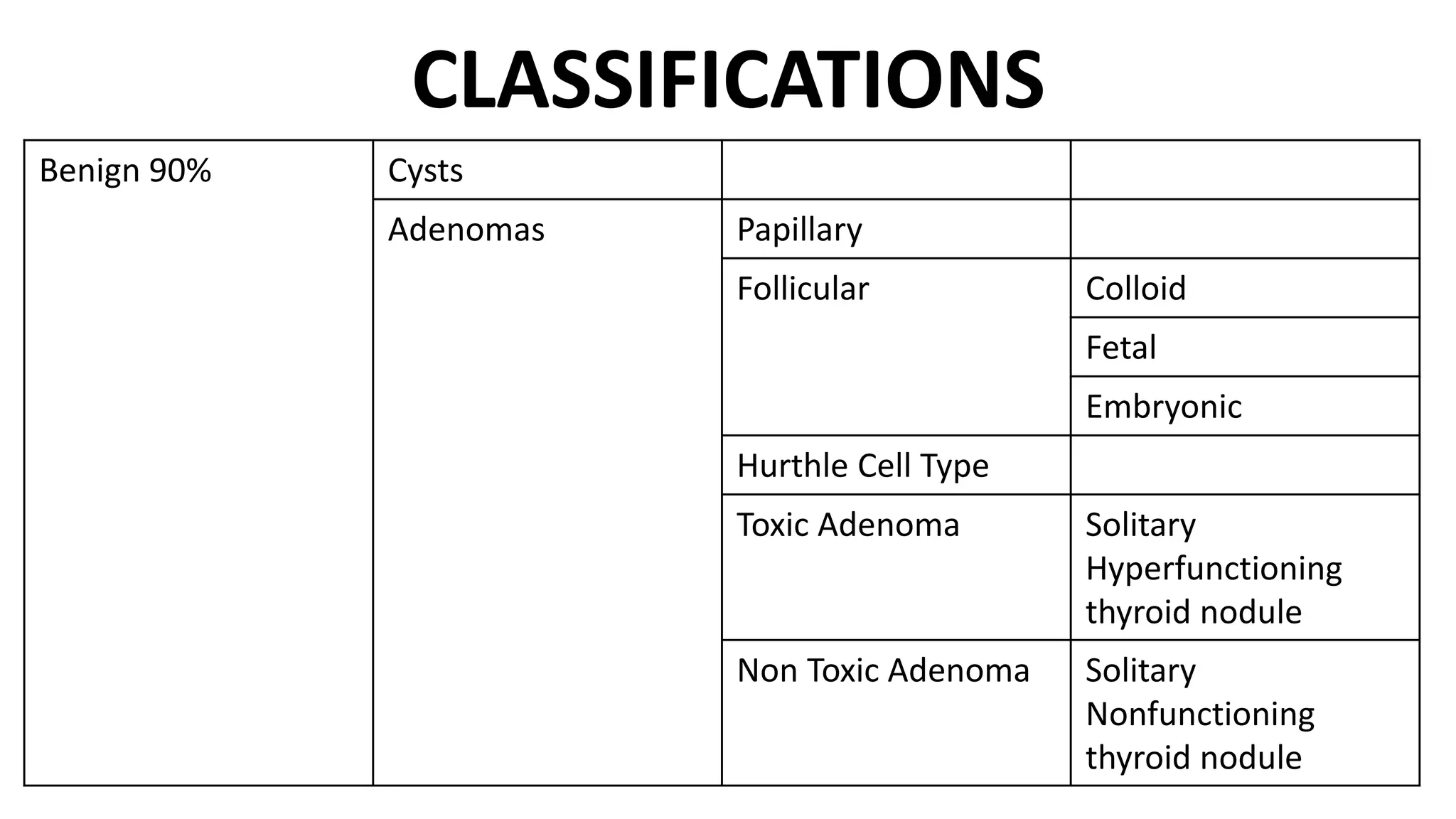
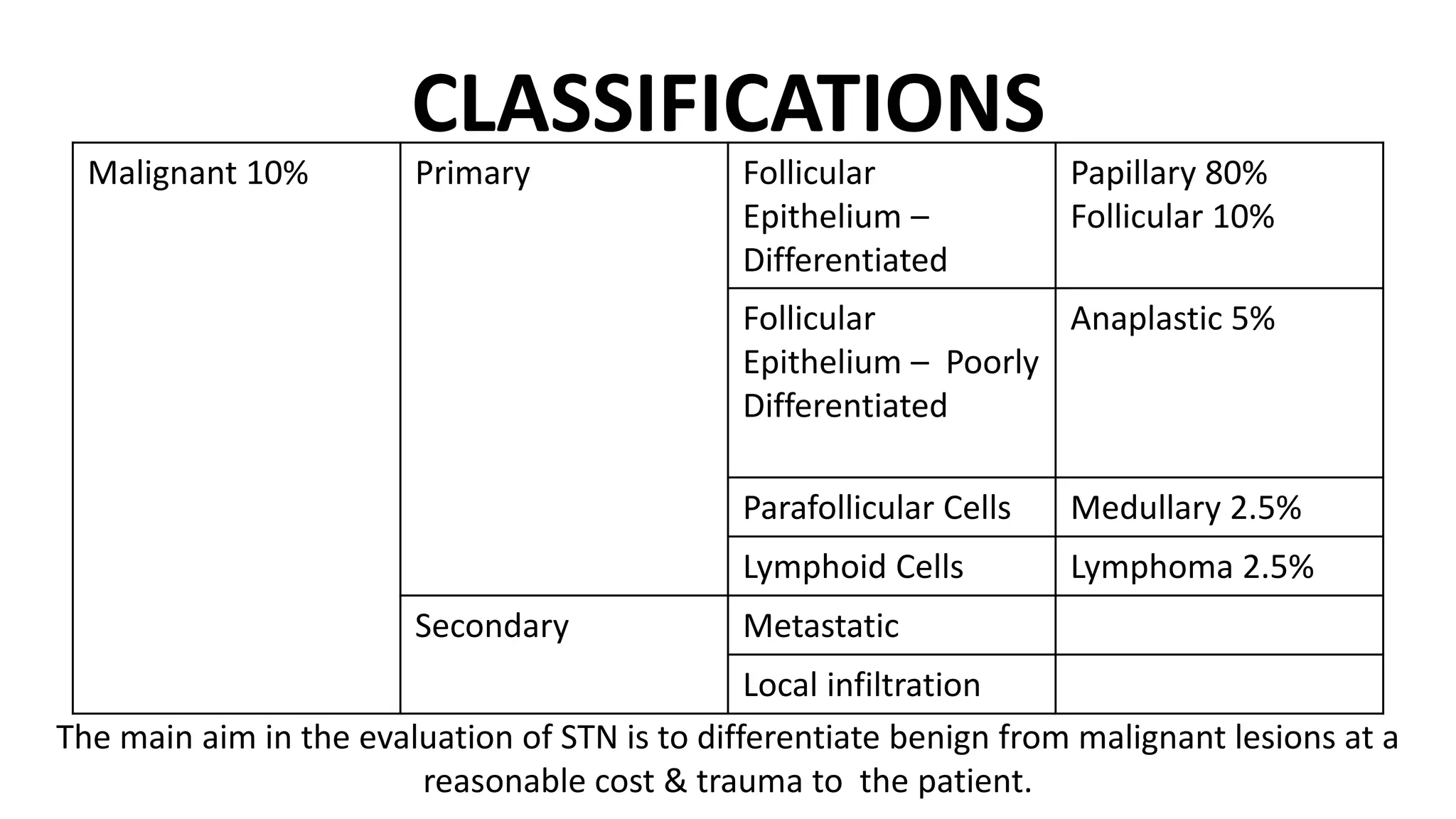
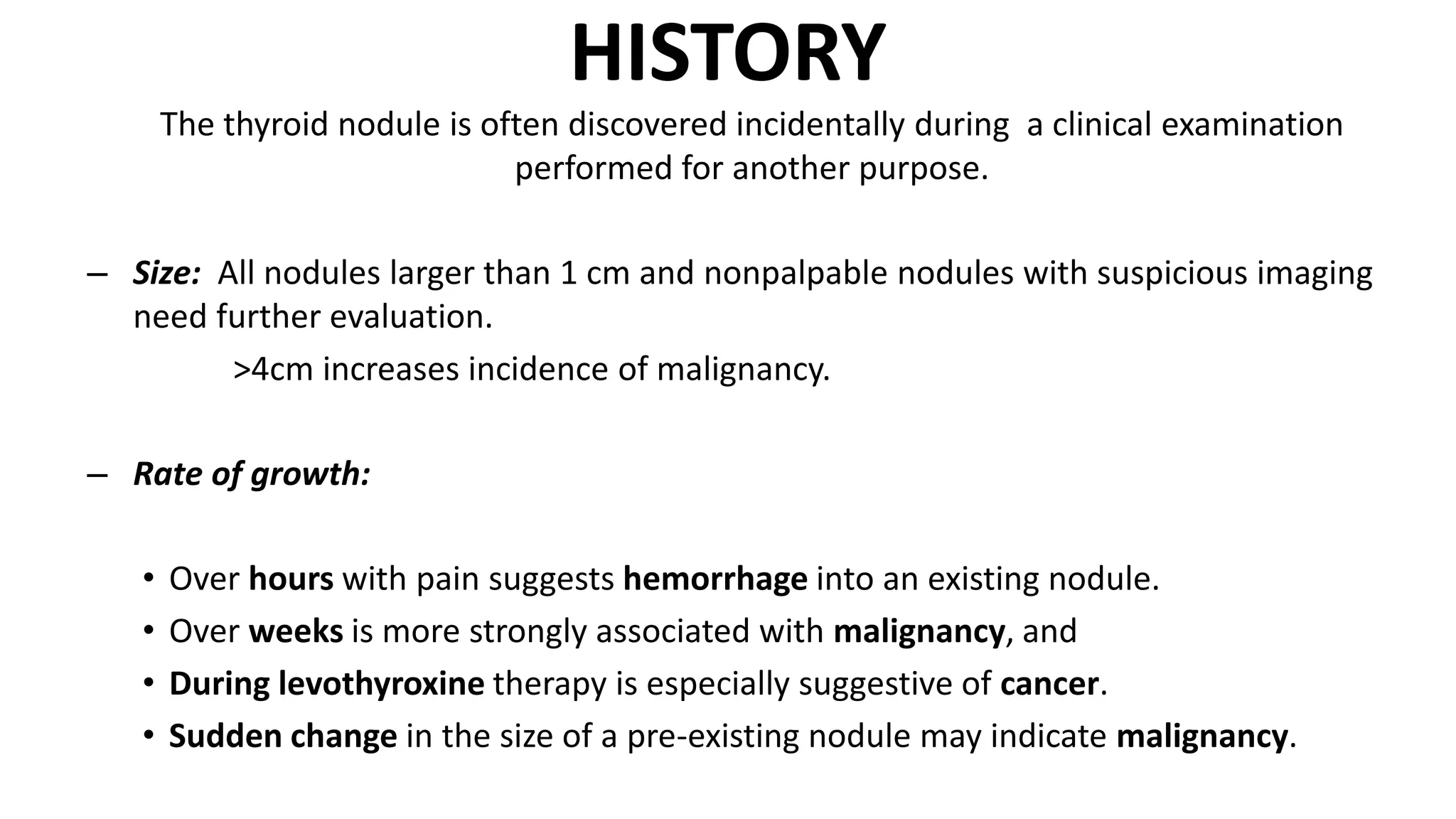
- Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is the most important diagnostic tool for evaluating a solitary thyroid nodule, as it is safe, cost-effective, and reliable for differentiating between benign and malignant diseases of the thyroid. Ultrasound-guided FNAC is more accurate than palpation-guided.
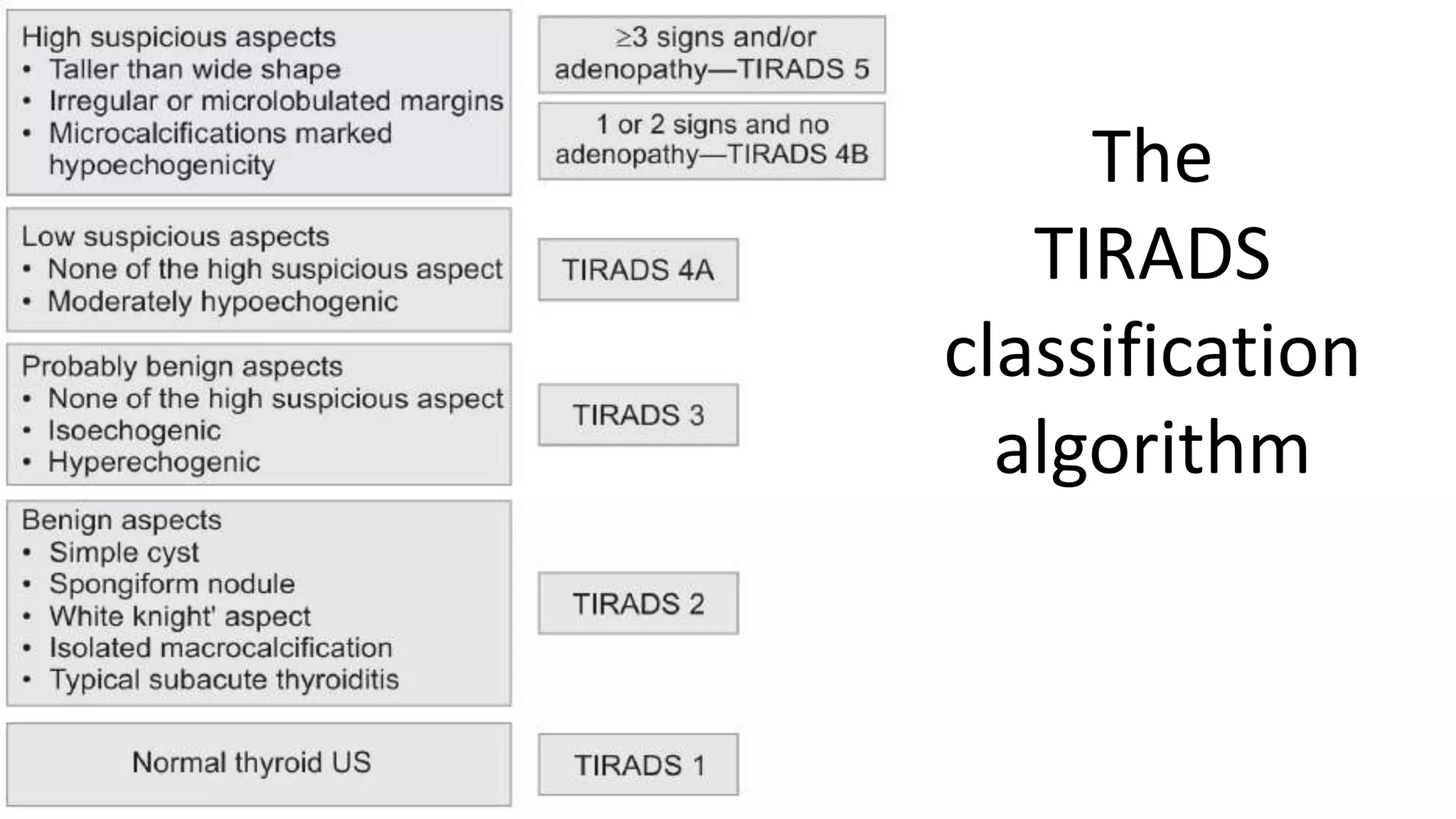
- Thyroid imaging with ultrasound and radioactive iodine uptake scans can identify high-risk features that increase the likelihood of malignancy, such as hypoechogenicity, microcalcifications, irregular shape, and lack of iodine uptake in the nodule.
- Cytology results are categorized using the Bethesda or THY classification systems. Suspicious or malignant results