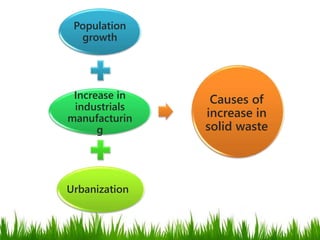
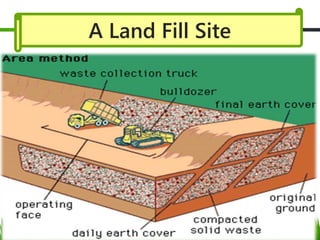
This document provides an overview of solid waste management. It defines the objective of solid waste management as controlling, collecting, processing, and disposing of solid waste in an economical way while protecting public health. It then classifies different types of solid waste such as municipal solid waste, biomedical waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste, and e-waste. The document discusses sources and collection of solid waste in India and the impacts of solid waste on health. It also examines causes of increased solid waste and different disposal methods like landfilling and incineration. Finally, it justifies the 3R concept of reduction, reuse, and recycling in municipal solid waste management.