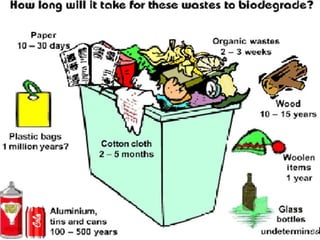
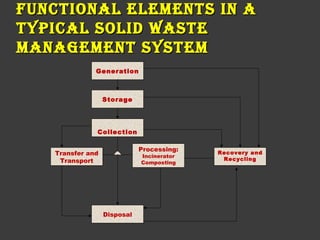
Solid waste includes organic and inorganic materials that are discarded because they have lost their value to the original user. Solid waste comes from residential, commercial, institutional, and other sources. It can be classified based on its source and type. Improper management of solid waste leads to air and water pollution and health issues. A solid waste management system includes generation, storage, collection, processing, and disposal. Processing techniques include incineration, composting, and landfilling. Proper waste management following rules of reduce, reuse, and recycle is needed.