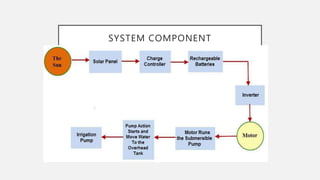
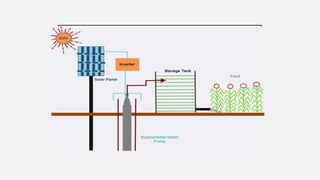
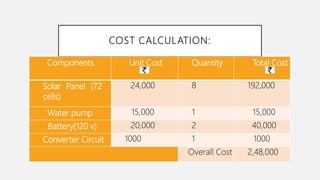
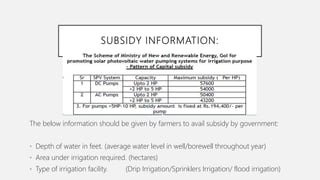
This document summarizes a solar powered automatic irrigation system for farmers. The key components are a solar panel to generate power, batteries to store the power, a water pump to pump water from a bore well to an overhead tank, and an automatic irrigation module using a moisture sensor. This module senses the soil moisture level and controls the water flow to irrigate the fields and optimize water usage. The system is self-starting and requires minimal maintenance as it uses solar power as a renewable energy source. It provides farmers with a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to grid-connected electricity for irrigation.