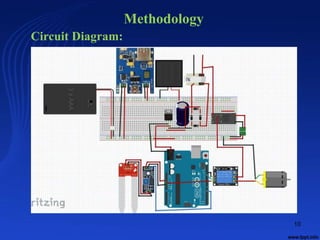
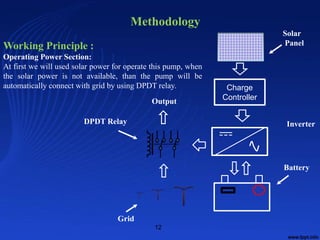
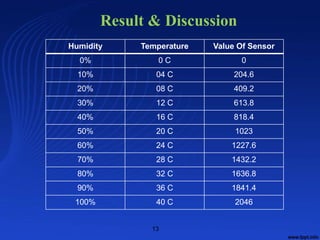
This document summarizes a student project on developing a solar power based automatic irrigation system using an Arduino. The system aims to minimize water wastage in agriculture by automatically irrigating crops based on soil moisture sensor readings. It uses a microcontroller, soil moisture sensor, relay switches, water pump, solar panel, battery, charge controller and inverter. The system measures soil moisture levels and turns the pump on or off to irrigate crops when the moisture level drops below a set threshold. It is powered by the solar panel but can also draw power from the grid through a relay switch if solar power is unavailable. The project aims to provide a low-cost and efficient irrigation solution to help farmers and reduce dependence on non-


![Introduction
Agriculture is the backbone of Bangladeshis economy.
It is one of the major occupations for many people in
Bangladesh. Out of 2/3rd water found on the Earth,
only 3.5% is fresh water that can be put into use in any
day-to-day activities. About 55% of this available
freshwater is used in agriculture and 10-30% of this
percentage gets wasted on a regular basis due to many
reasons. Over the years different means of irrigation has
evolved to minimize this wastage of water in
agricultural lands. However, one of the major problems
that still remains, leading to wastage of water, is the
lack of proper knowledge of the farmers about the soil
moisture content, and hence the requirement of the
amount of water in the agricultural soil. [2] Moreover,
due to lack of irrigation the crop to be very low, it's
happen to the load shading. it can be reduced used solar
power system. The global irrigation scenario is
categorized based on increased demand for higher
agricultural productivity and decrease the availability of
water and power.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arif-191201122857/85/Solar-Power-Based-Automatic-Irrigation-System-3-320.jpg)









![[1]Solar,Photovoltaic_system[Online].Available:https://en.wikipedia
.org/wiki/Photovoltaic_system (Visited on 01/12/2018)
[2]Solar,PV_system,[Online],Available:http://www.fsec.ucf.edu/en/c
onsumer/solar_electricity/basics/how_pv_system_works.htm(Visited
on 02/12/2018)
[3]ChargeController,solar_system,[Online]Available:https://www.sol
ar-electric.com/learning-center/batteries-and-charging /solar-charge-
controller-basics.html(Visited on 5/12/2018)
Reference
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arif-191201122857/85/Solar-Power-Based-Automatic-Irrigation-System-16-320.jpg)
