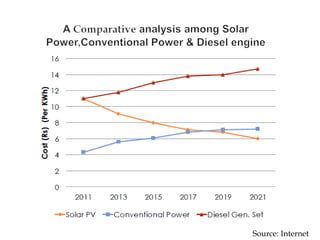
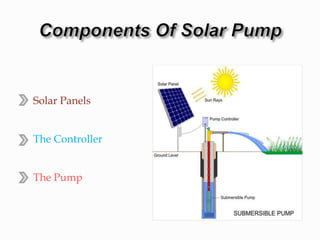
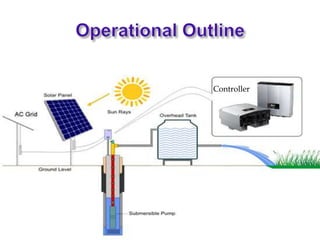
The presentation discusses the advantages of solar water pumps, which are powered by electricity generated from solar panels and are more economical and environmentally friendly compared to traditional diesel pumps. It highlights the significant electricity consumption in the agriculture sector in India and the potential for solar pumps to replace diesel pumps, which can reduce pollution and operational costs. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy plans to implement solar pumps with subsidies for farmers to promote sustainable irrigation practices.