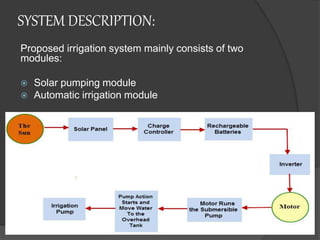
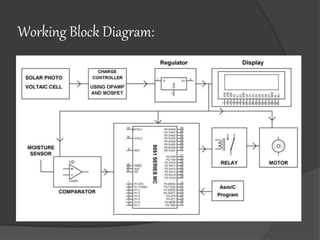
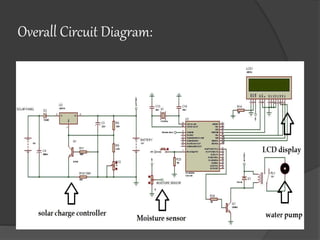
Pankaj Kumar presents on a solar powered automatic irrigation system. The system uses solar panels to generate electricity which powers a submersible pump to pump water from a bore well to a storage tank. A soil moisture sensor and microcontroller are used to automatically regulate the flow of water from the tank to irrigate fields, optimizing water usage. The system aims to provide farmers an alternative irrigation method that is powered by solar energy and reduces reliance on manual labor.