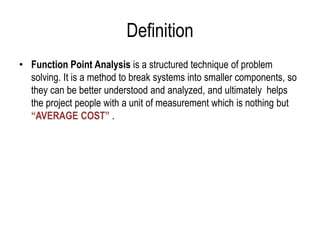
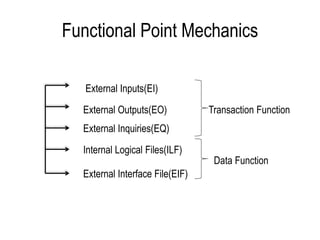
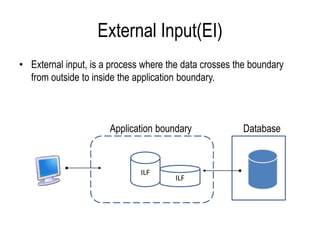
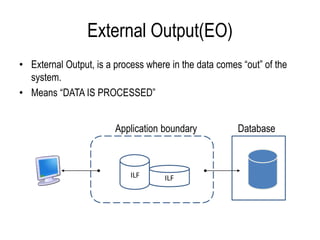
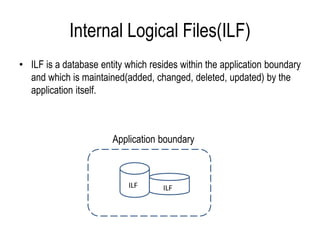
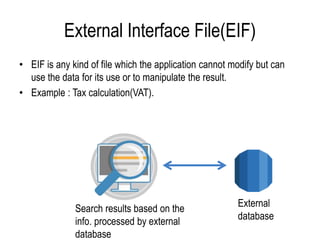
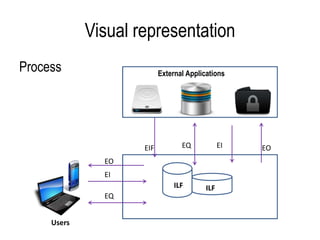
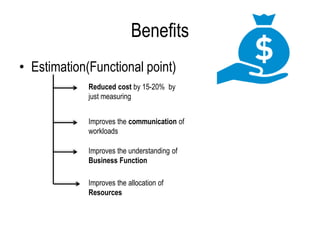
The document explains software estimation techniques, including Delphi, work breakdown structure, and functional point method, focusing on functional point analysis as a structured problem-solving technique. It outlines the steps to count function points, emphasizing the importance of understanding user requirements and data processing within applications. Ultimately, it highlights that function points are essential for measuring software size, improving cost efficiency, communication, resource allocation, and enhancing productivity and quality in software development.