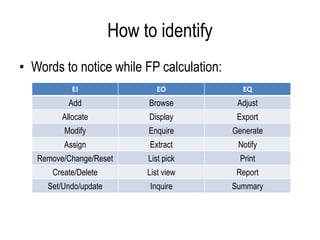
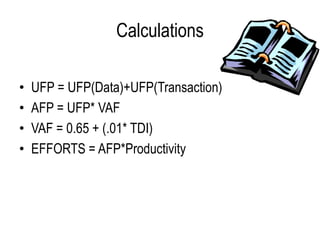
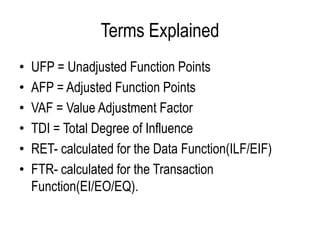
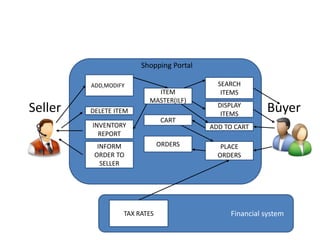
The document provides steps and guidelines for calculating function points for a system. It explains that function point counting involves identifying the number of external inputs, external outputs, external inquiries and internal logical files and external interface files, and determining their complexity based on factors like file and transaction types and records and determinants. The document then provides complexity matrices and formulas to calculate the unadjusted function points, adjusted function points based on a value adjustment factor, and efforts based on productivity. It also defines key terms used in function point analysis.