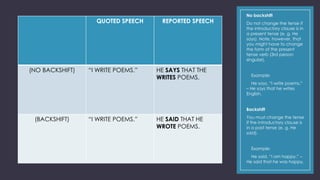
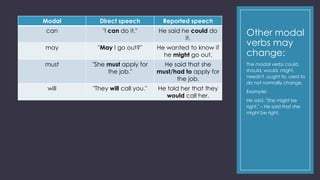
1) When transforming statements from direct to reported speech, you may need to change pronouns, tenses, and references to place, time, and demonstratives.
2) Pronouns often need to change depending on who is speaking. Tenses typically change from present to past if the statement is being reported about something said in the past.
3) References to place, time, and demonstratives may need to change if the context has shifted from when the direct statement was made.