Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times

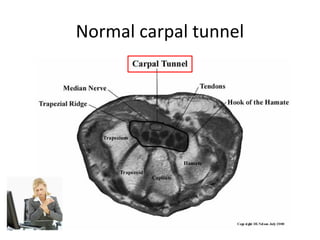
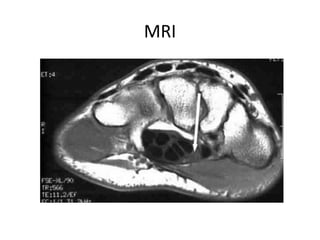
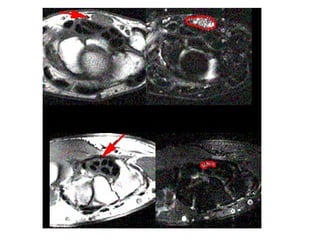
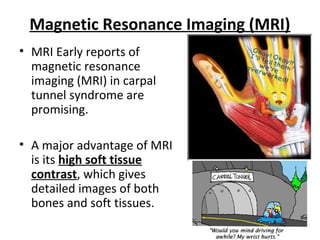
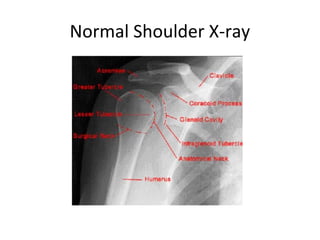
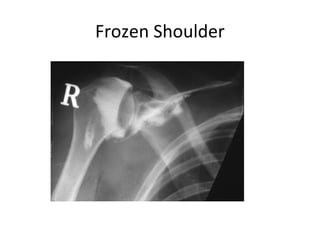



This document discusses carpal tunnel syndrome and frozen shoulder. For carpal tunnel syndrome, it describes the normal carpal tunnel anatomy, MRI as a promising imaging technique due to its high soft tissue contrast, and potential treatments including splinting, corticosteroids, surgery, and physiotherapy. For frozen shoulder, it shows normal and affected shoulder x-rays, and lists treatments such as keeping the shoulder moving, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, exercises, hydrodilatation injections, and surgery.











