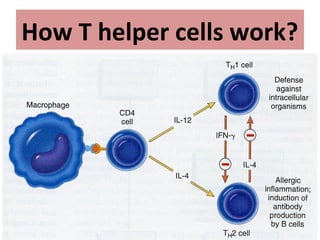
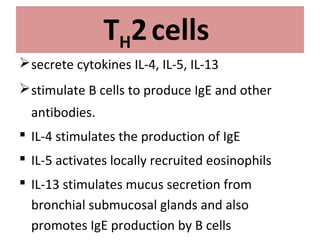
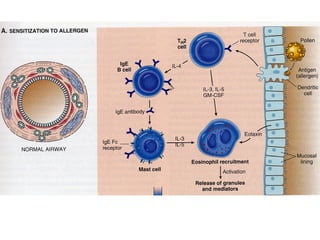
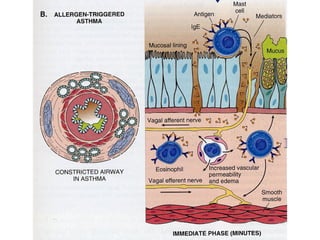
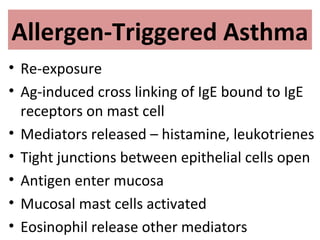
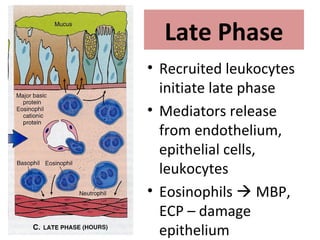
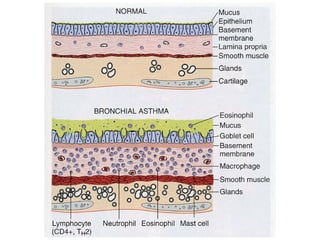
TH2 cells secrete cytokines like IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 that stimulate B cells to produce IgE antibodies and recruit eosinophils. Upon exposure to allergens, IgE binds to mast cells, which then release mediators like histamine and leukotrienes upon re-exposure. This causes bronchospasm, edema, and mucus production. In the late phase, recruited leukocytes release more mediators that damage the epithelium. In asthma, there is thickening of the basement membrane, accumulation of mucus, and chronic inflammation from increased eosinophils and goblet cells.