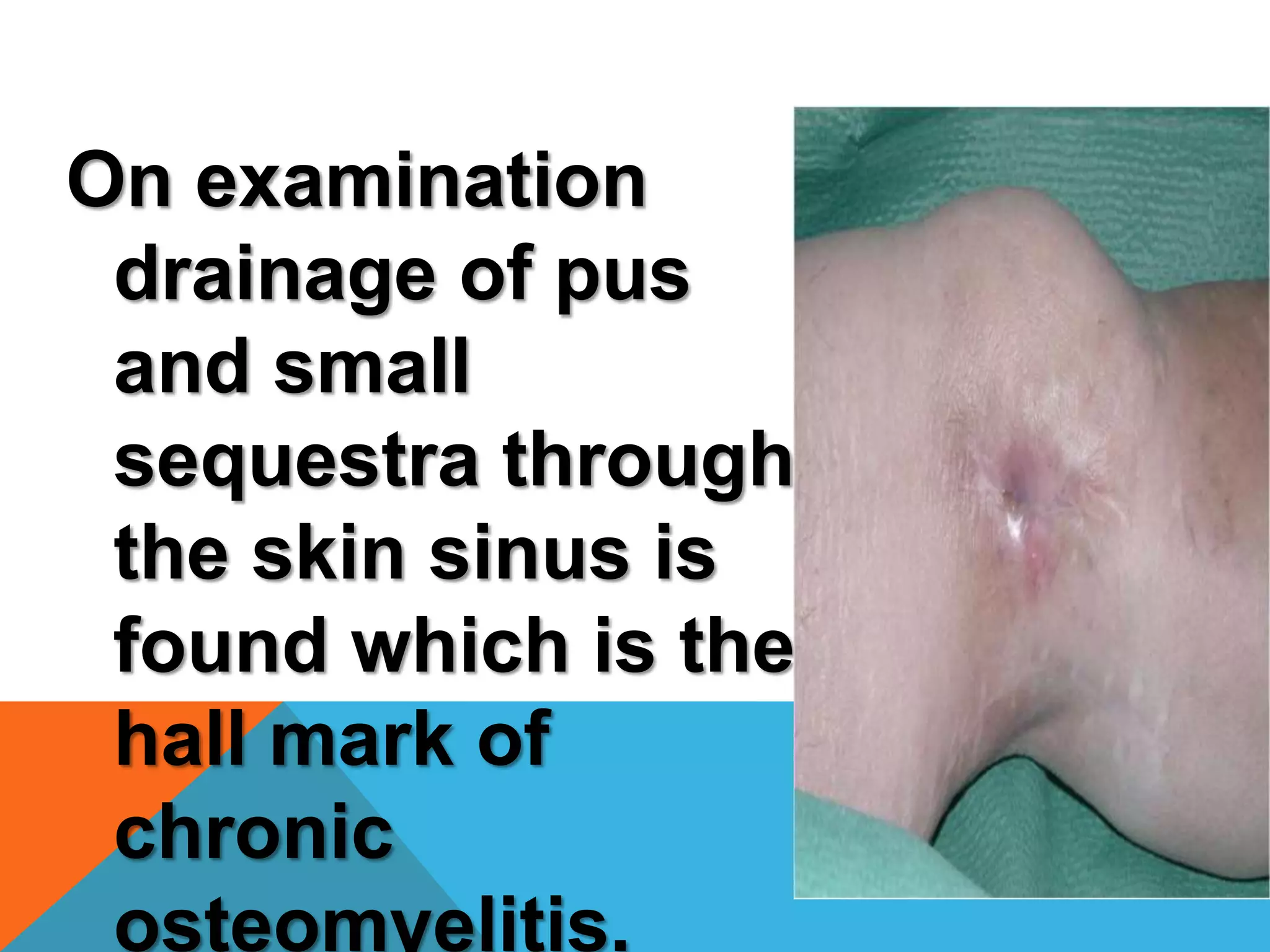
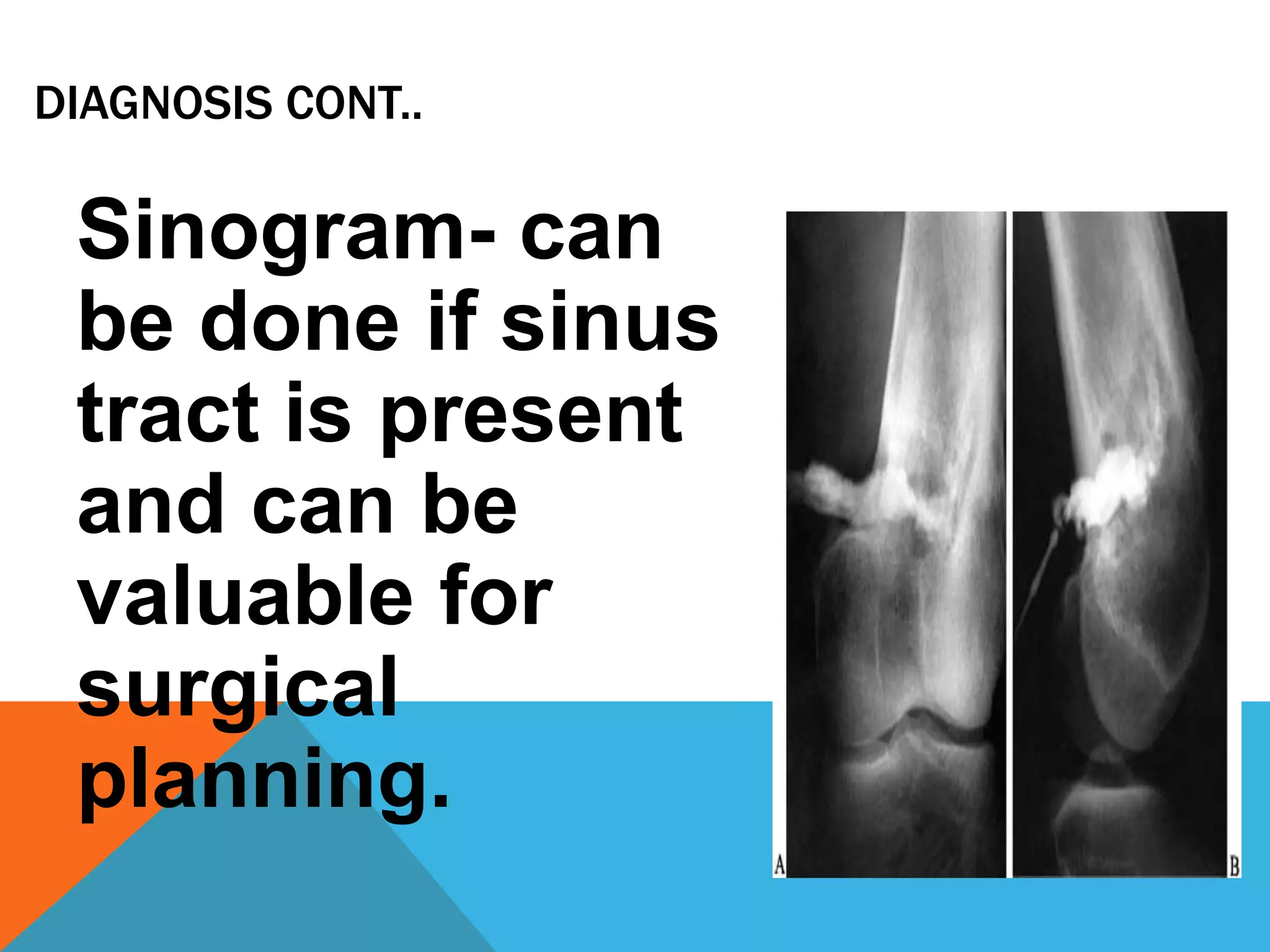
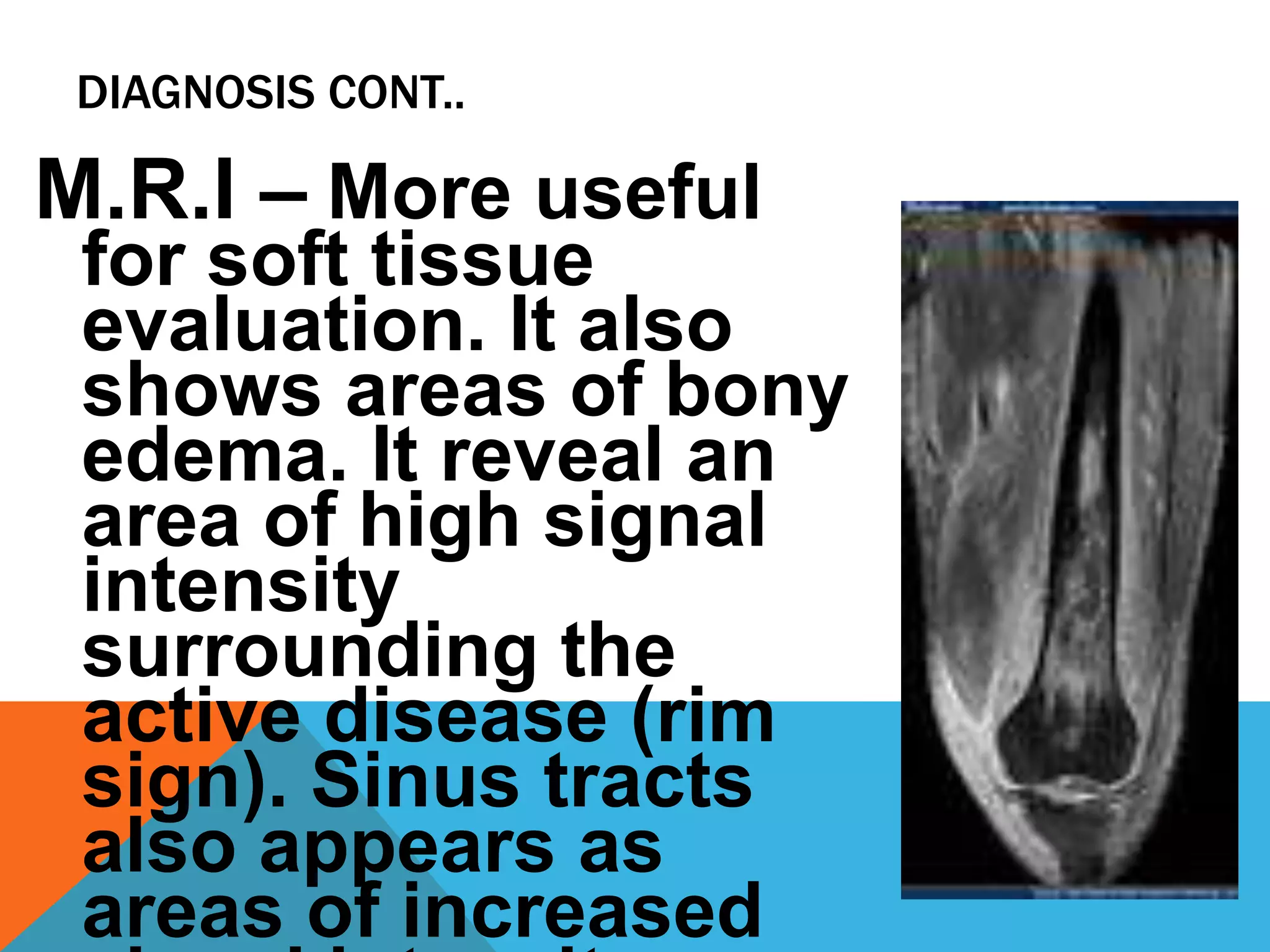
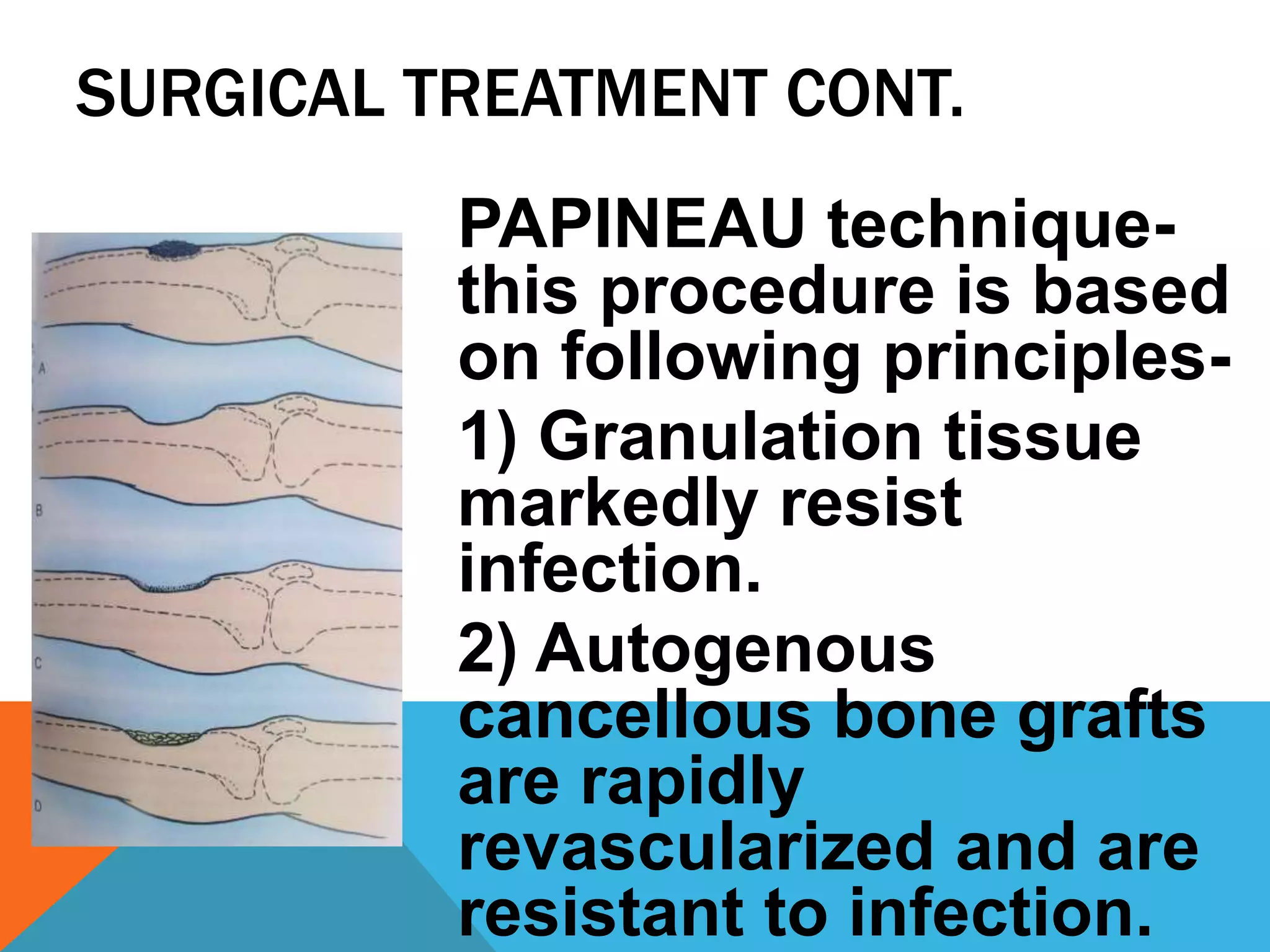
Chronic osteomyelitis is a bone infection lasting over 6 weeks. It is characterized by recurrent inflammation, draining sinuses, and dead bone. Common causes are Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria. Over time, the infection causes bone necrosis and formation of sequestra - dead bone pieces. Surgical treatment aims to thoroughly debride infected tissue, remove sequestra, and reconstruct the bone defect. Antibiotic therapy and soft tissue coverage are also important for treatment. Complications can include pathological fractures, deformity, and malignant transformation if not properly treated.