This document discusses sociological approaches to understanding social structure and social interaction from both a macro and micro perspective. [1] It explores how macrosociology examines the larger framework of society, including social structure defined by factors like culture, class, status, roles, groups, and institutions. [2] Microsociology focuses on face-to-face interactions and behaviors influenced by concepts like stereotyping, personal space, and body language. [3] Both approaches are necessary to understand how social realities are constructed and how social structure guides interactions.

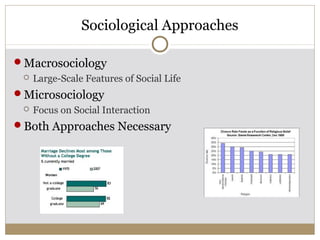






![The Social Construction of Reality
Our own subjective reality
http://youtu.be/myq8upzJDJc Josh Bell in the Metro
http://vimeo.com/16329078 Up in the Air
Thomas Theorem
How does stereotyping play out?
Using a famous quote known as the Thomas theorem, we can
begin to understand the potentially damaging effects of
stereotypes: "if [people] define situations as real, they are real in
their consequences." In other words, when people accept
stereotypes as true, then they are likely to act on these beliefs, and
these subjective beliefs can lead to objective results.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socialstructureandintegration-130128080934-phpapp02/85/Social-structure-and-social-interaction-9-320.jpg)

