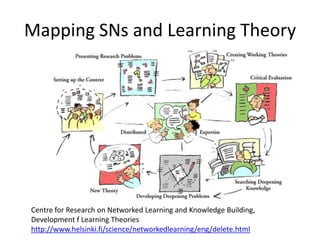
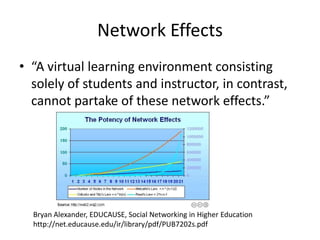
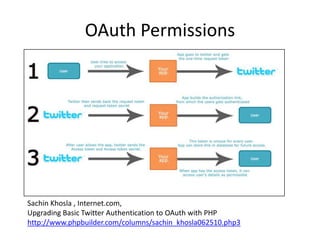
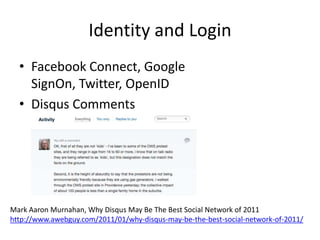
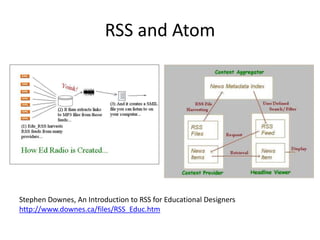
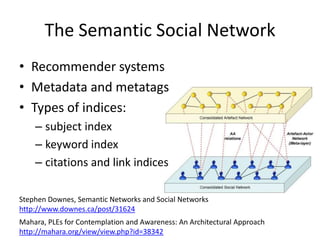
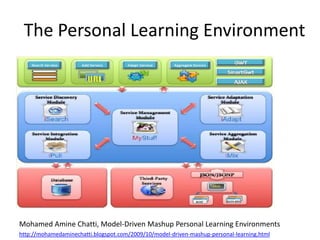
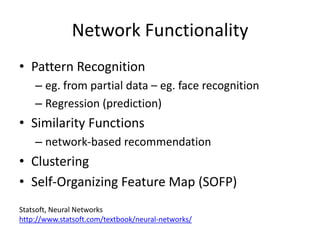
The document discusses social networks and their potential applications for learning. It begins by describing major existing social networks like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. It then explains key elements of social networks like personal profiles, connections between users, actions users can take, and sharing content. The document outlines both benefits and risks of using social networks for education. It presents examples of how social networks can enhance learning through connection, collaboration, and crowdsourcing. Finally, it explores platforms and programs that enable social network functionality for learning applications and the emergence of distributed and personalized learning networks.