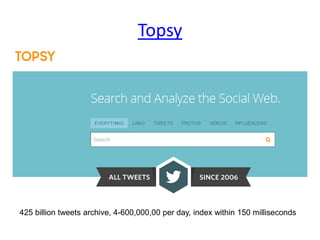
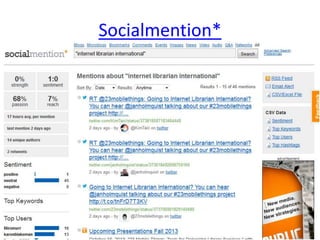
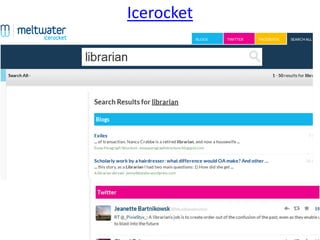
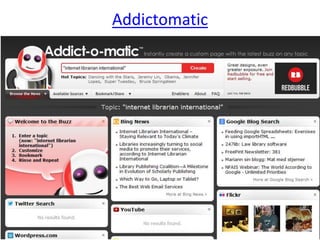
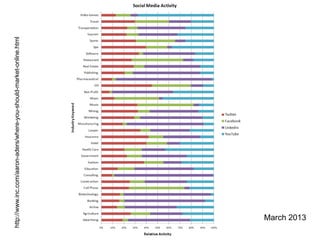
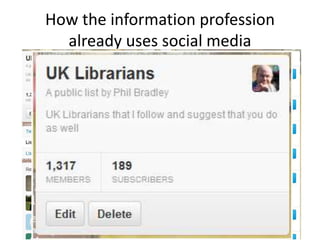
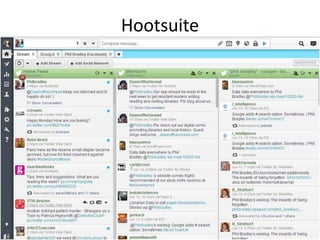
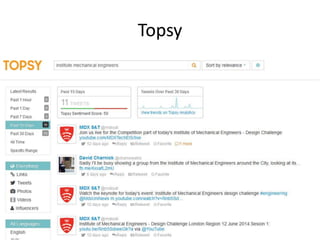
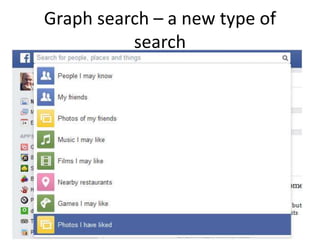
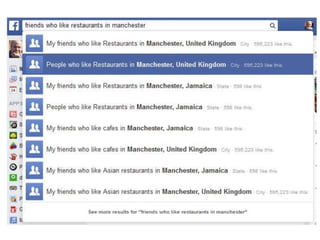
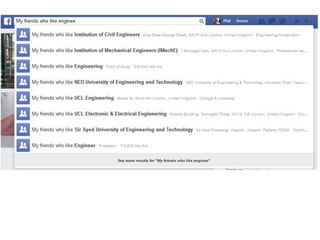
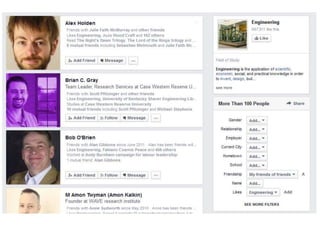
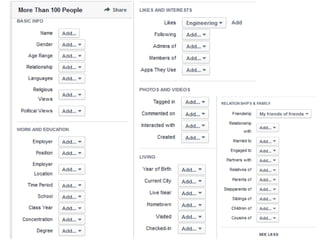
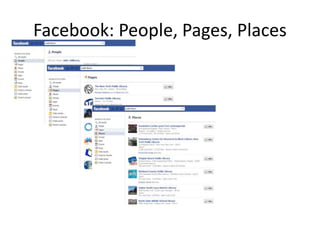
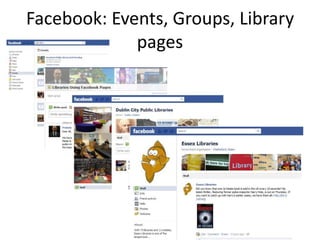
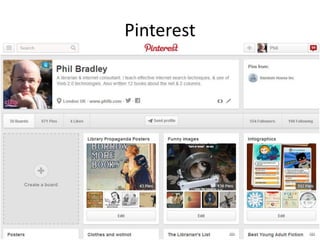
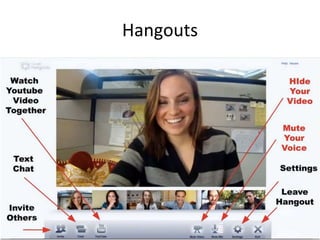
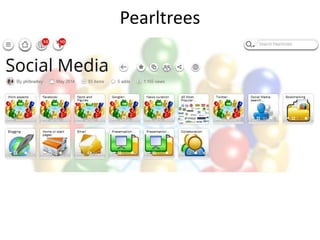
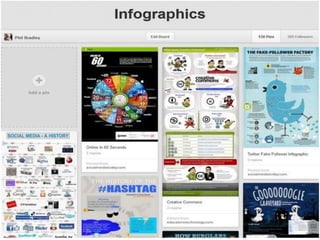
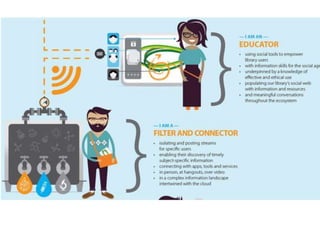
The document discusses the shift from traditional websites to social media platforms. It outlines how social media allows for more interactive and user-generated content compared to the older top-down model of websites. Examples are given of how libraries and information professionals are now using social tools like blogs, Twitter, Facebook, Pinterest and curation tools to connect with users and stay up-to-date. The importance of individuals and real-time conversations on social networks is highlighted as search rankings and information gathering become increasingly based on social signals and interactions.