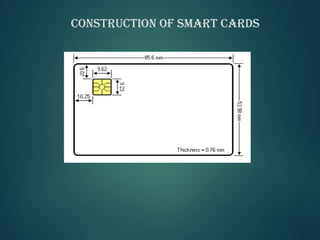
Smart cards are credit card sized devices with embedded microchips that can store and process data. They come in two varieties, memory-only chips and microprocessor chips, and can hold up to 32,000 bytes of data. Smart cards interact with card readers, either computer based USB readers or dedicated terminals with screens and keypads. They are used for applications like payments, identification, financial services, and communication. Advantages of smart cards include large memory capacity, security, reliability, and portability, but disadvantages are the risk of theft or loss and lack of tamper proofing.