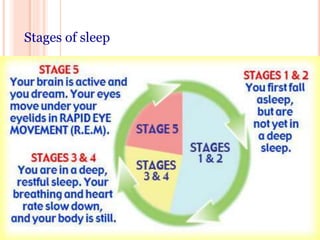
Sleep is a natural behavior that is divided into stages and is important for physical and mental health. Lack of sufficient sleep, known as sleep deprivation, can be caused by factors like medication, lifestyle, caffeine, and stress. Effects of sleep deprivation include increased risk of health issues like heart disease and diabetes, as well as mental impacts such as impaired memory, mood changes, and reduced cognitive performance. To avoid sleep deprivation, one should exercise regularly, take naps, maintain a consistent sleep schedule, and reduce caffeine and alcohol intake close to bedtime.