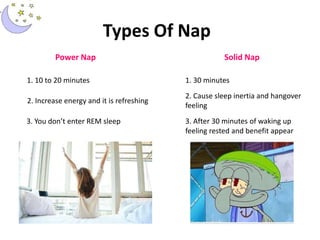
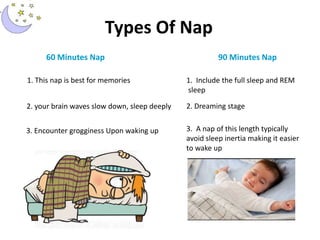
This document provides information about sleep, including what sleep is, the sleep cycle, types of normal and abnormal sleep, and tips for improving sleep. Key points include:
- Sleep is a condition where the body and mind rest that typically occurs at night for 7-9 hours. It is essential for survival.
- The sleep cycle progresses through NREM and REM sleep stages roughly every 90 minutes over 4-5 cycles per night.
- Normal sleep means falling asleep within 20 minutes, sleeping 7-9 hours continuously, and waking feeling refreshed.
- Tips for better sleep include avoiding screens before bed, using yellow light, sticking to a schedule, and being in a dark, cool room.