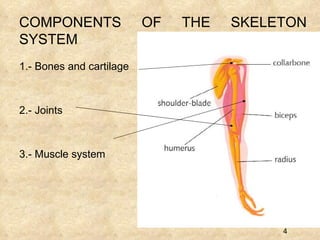
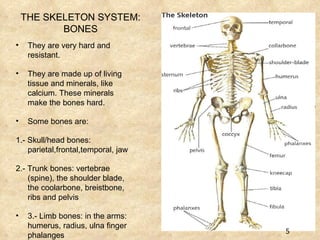
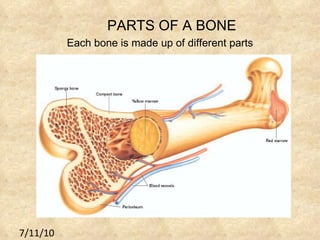
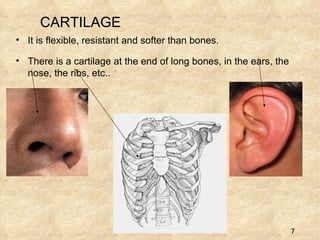
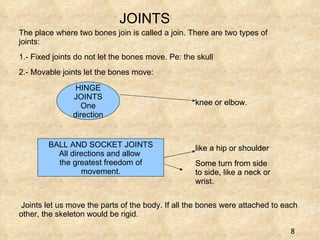
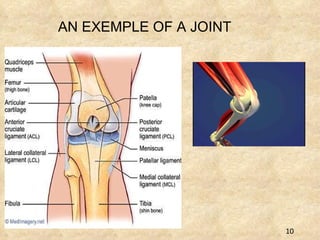
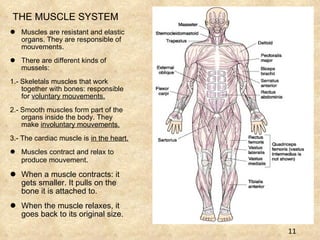
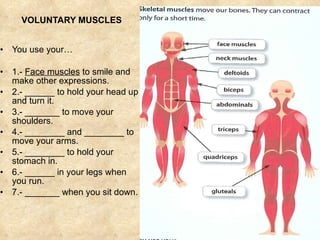
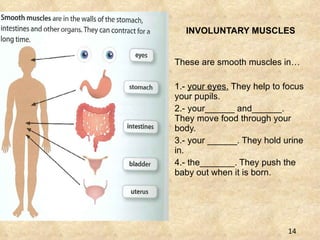
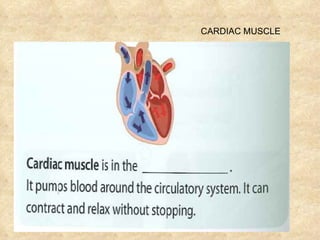
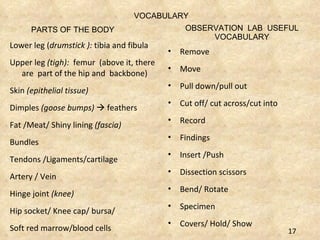
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the human motor system. It discusses that the skeletal system provides support, protection, movement, storage, and production of blood cells. The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilage, and joints. Bones are made of living tissue and minerals. Joints connect bones and allow movement, with examples being ball-and-socket and hinge joints. Muscles work with bones to enable movement. The nervous system controls voluntary and involuntary muscle movement.