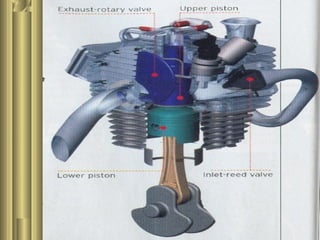
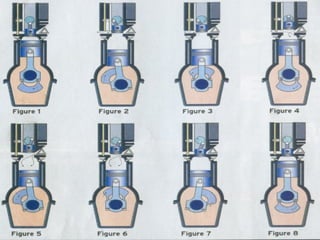
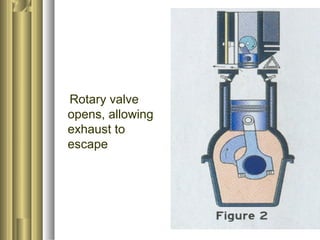
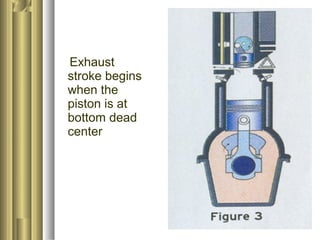
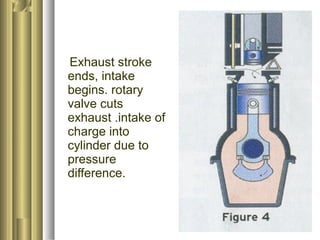
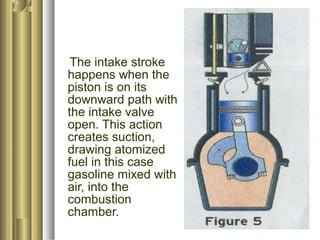
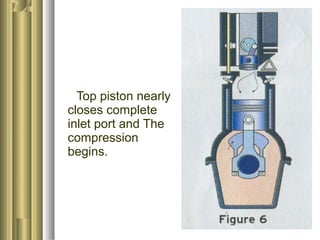
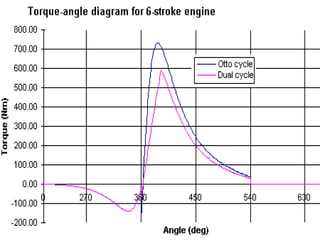
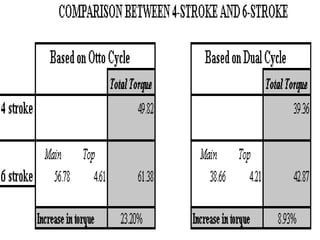
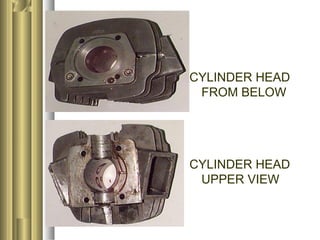
The document discusses the innovative six-stroke engine developed by Malcolm Beare, which combines features of two-stroke and four-stroke engines, leading to increased power and torque while simplifying engine design. Key benefits include reduced complexity, fewer engine parts, and greater thermodynamic efficiency compared to traditional engines. The six-stroke engine can be retrofitted onto existing four-stroke engines with minimal modifications, making it a cost-effective alternative in engine technology.