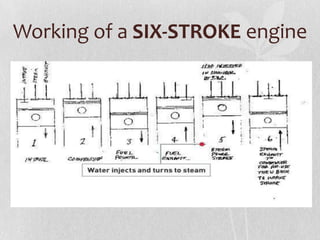
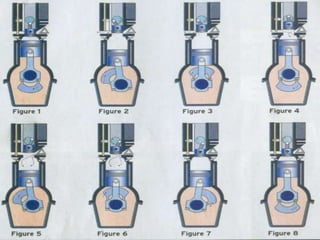
The six-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine that builds upon the four-stroke engine design to increase efficiency. It has two approaches - the first uses the same piston for two additional strokes, while the second uses a second opposed piston moving at half the rate of the main piston. The six-stroke engine injects water into the combustion chamber on the power stroke, turning it instantly into steam for an additional power stroke. This provides increased efficiency over traditional engines by extracting work from heat otherwise lost and reducing emissions and fuel consumption by up to 40%. However, challenges include potential piston damage from thermal expansion and ensuring an adequate water supply.