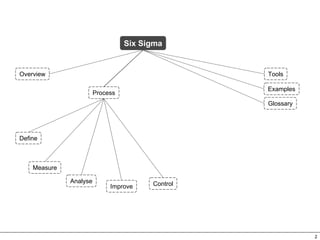
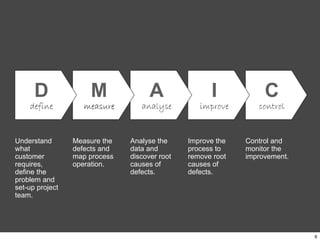
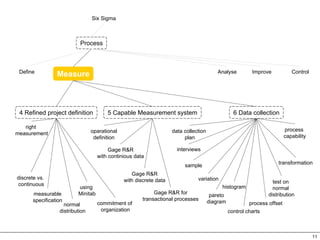
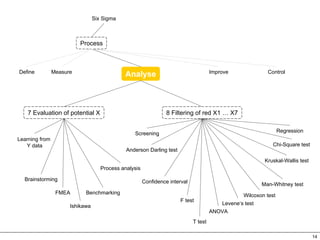
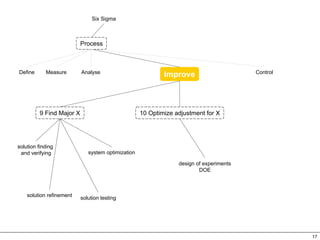
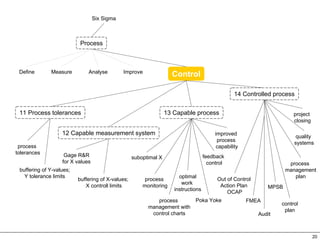
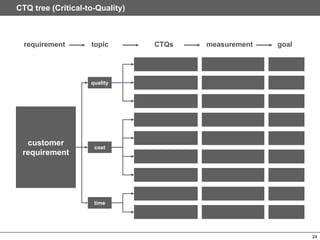
This document provides an overview of Six Sigma, which is a data-driven methodology for improving business processes and products. It involves five phases - Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control - and utilizes statistical tools to measure defects and understand their root causes. The goal is to continuously improve processes by removing defects based on data analysis, and then controlling processes to maintain improvements.