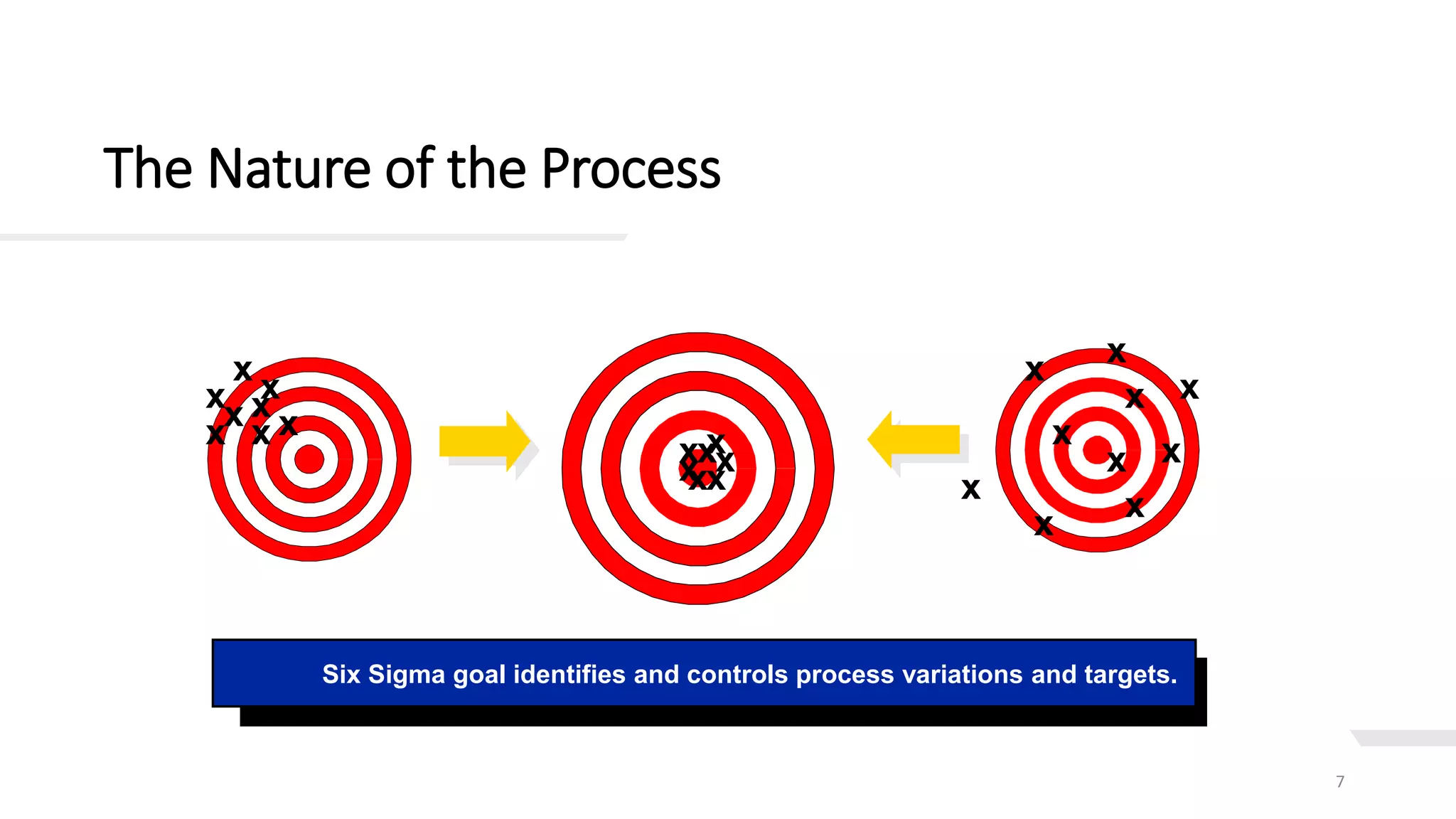
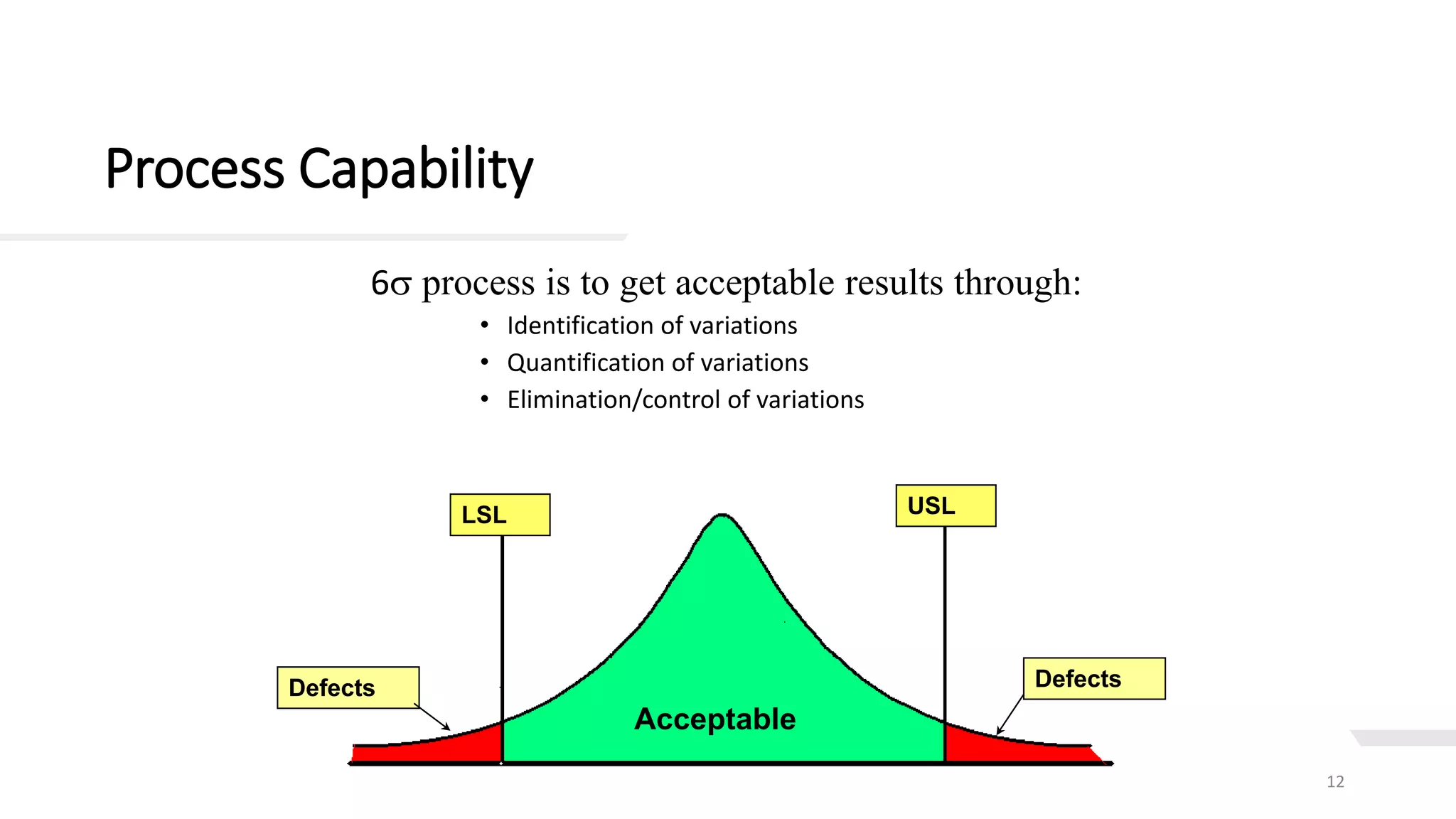
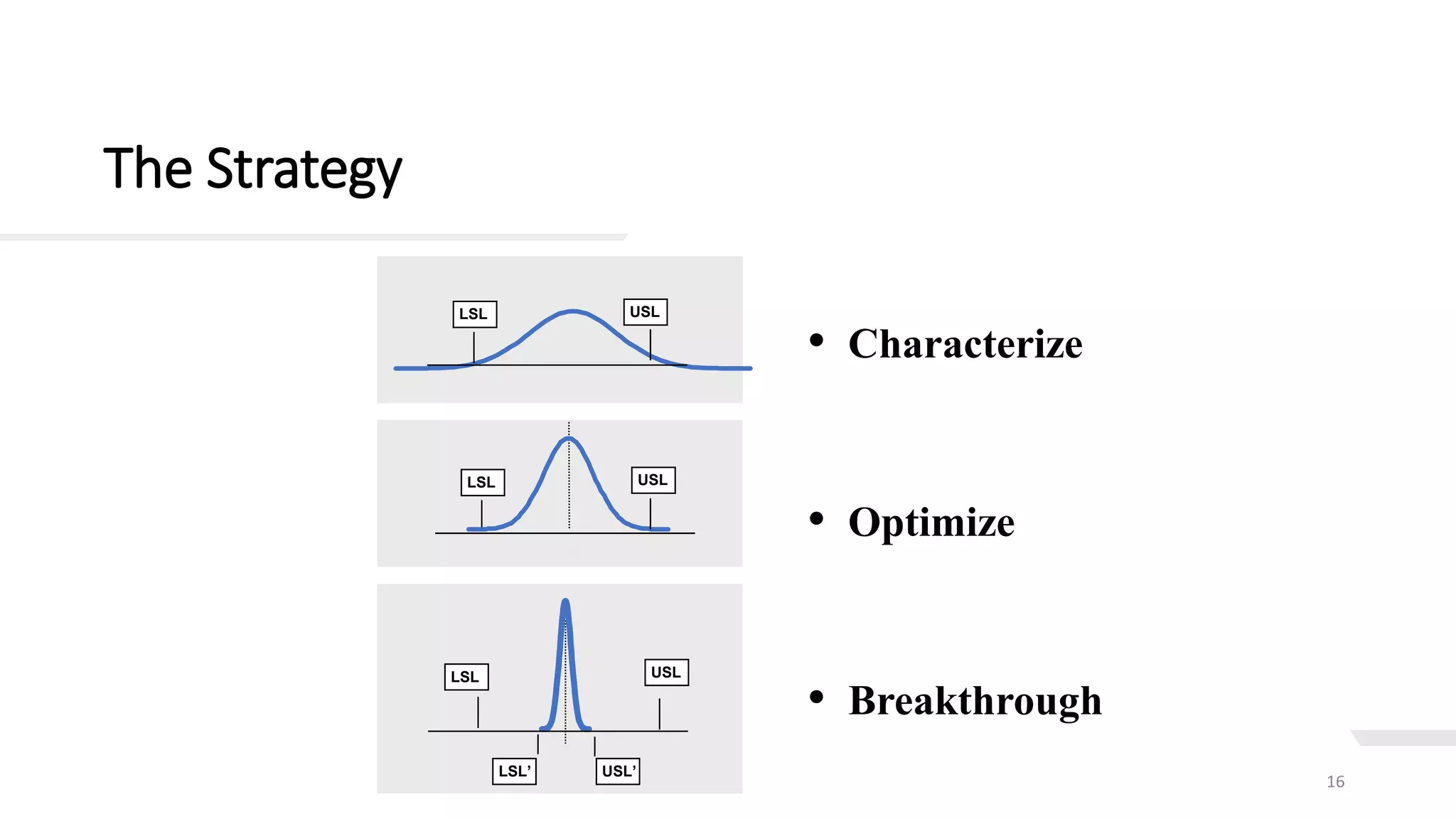
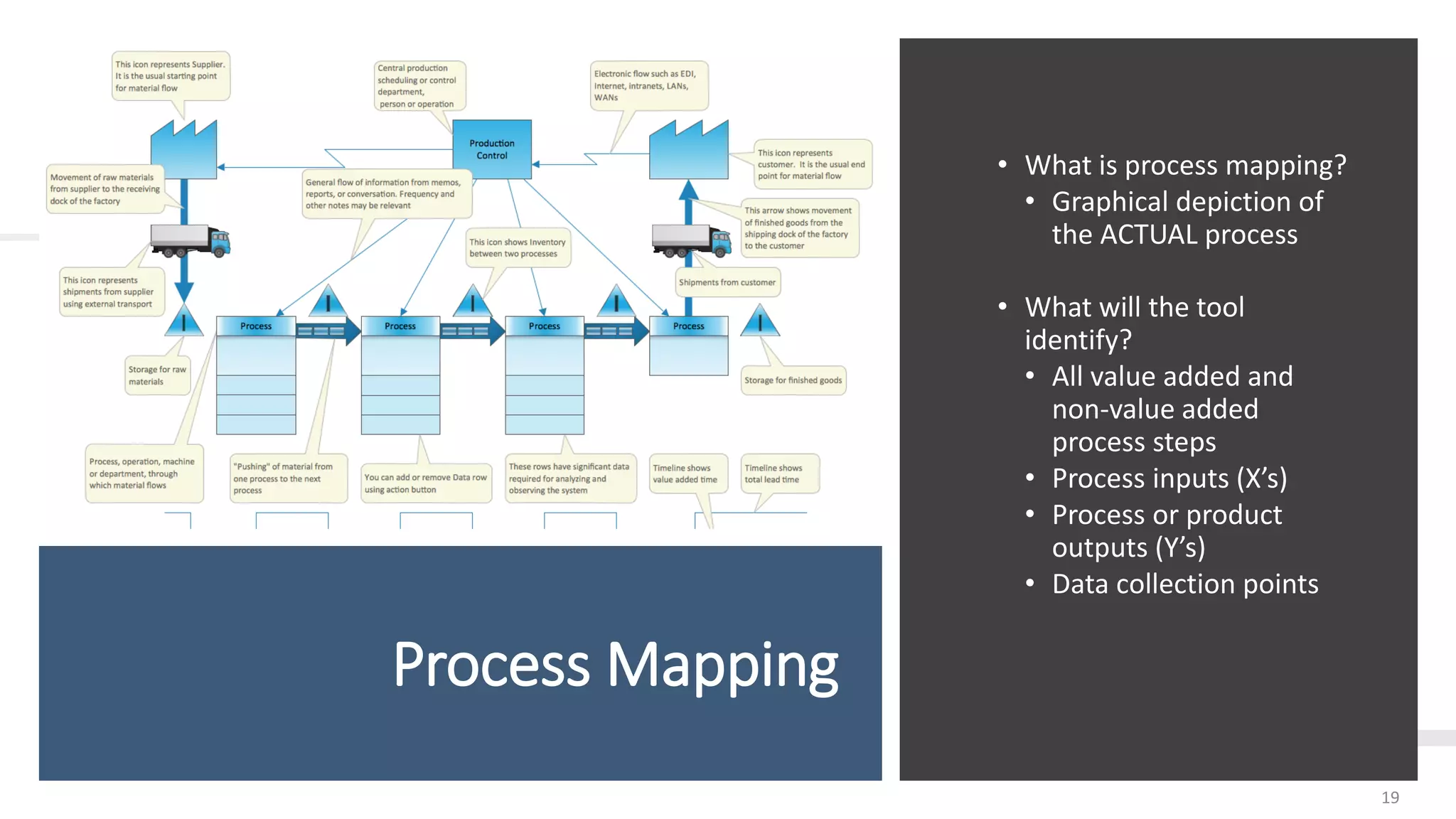
This document provides an overview of Six Sigma, including definitions of key terms, approaches, and phases. It describes Six Sigma as a data-driven methodology to reduce defects by identifying and removing sources of variation. The summary phases are:
1. Measurement phase involves identifying key inputs/outputs, defects, and process capability to establish a baseline.
2. Analysis phase examines the process and data to determine the root causes of problems through tools like histograms and ANOVA.
3. Improvement phase designs experiments to address root causes and select the most impactful solutions.
4. Control phase develops long-term methods like control plans and SPC to sustain gains.