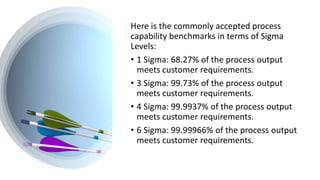
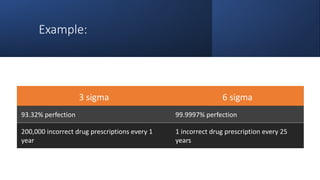
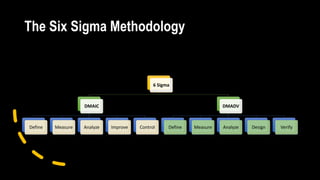
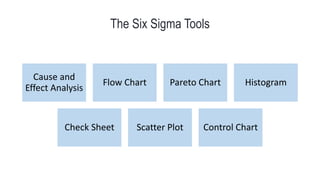
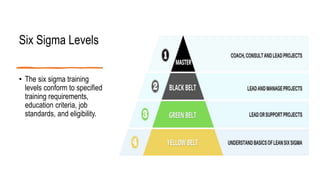
Six Sigma is a methodology that aims to improve processes and minimize defects. It uses a data-driven approach called DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to identify and address sources of variation. The goal of Six Sigma is to achieve nearly perfect processes with fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It was developed by Motorola to improve quality and has since been widely adopted. Key aspects of Six Sigma include defining problems, measuring processes, analyzing sources of variation, improving processes, and controlling improvements.