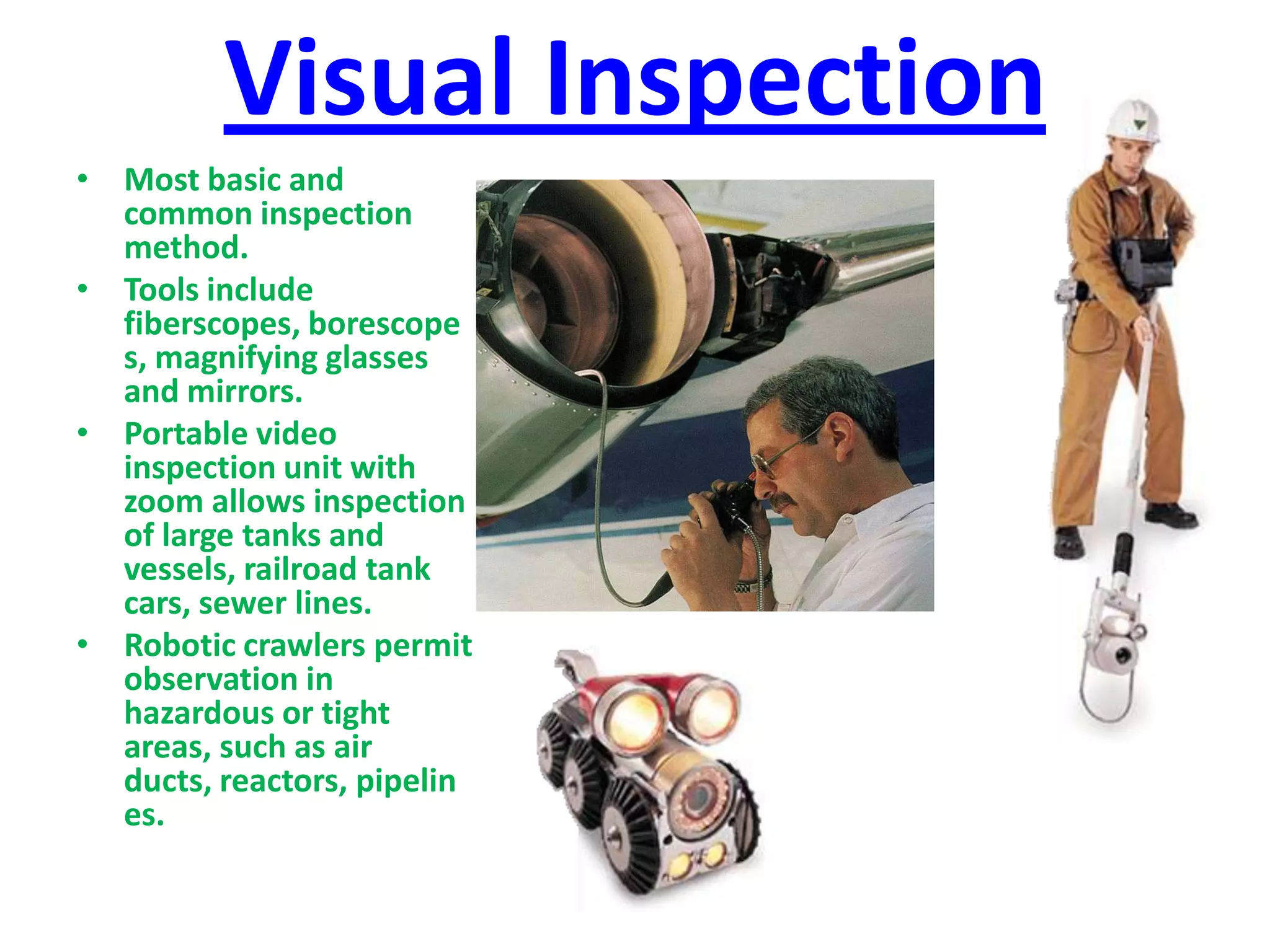
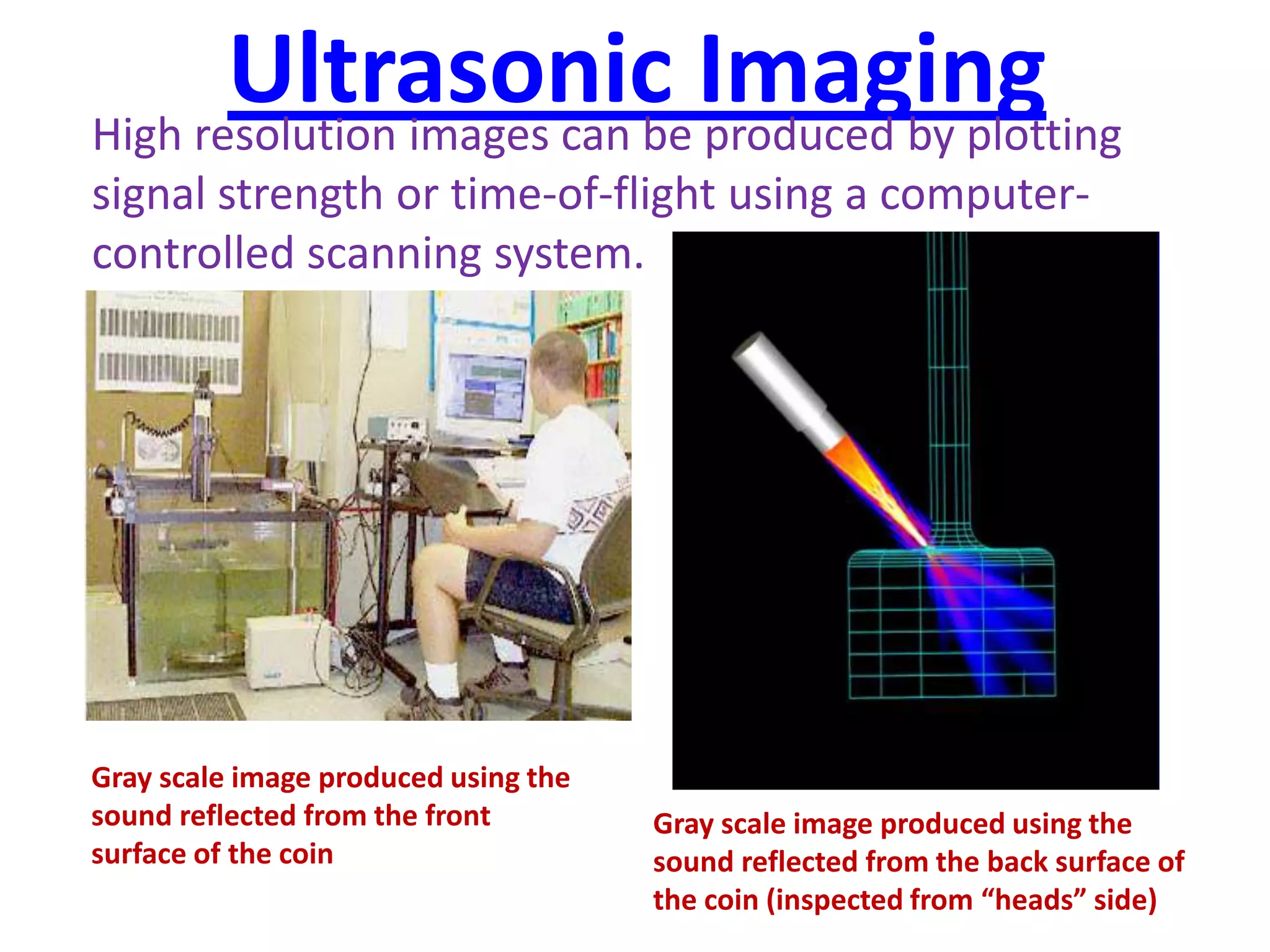
The document outlines six common non-destructive testing (NDT) methods: visual, liquid penetrant, magnetic particle, ultrasonic, eddy current, and x-ray inspections. Each method is detailed in terms of its process, tools, and specific uses, highlighting the techniques involved for detecting surface defects. It also provides contact information for further inquiries about NDT services in India.