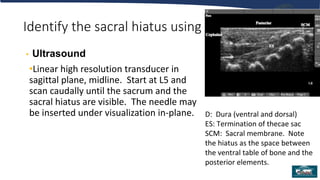
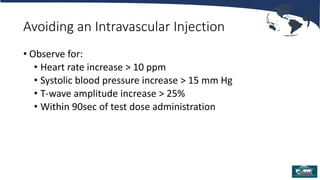
Single injection caudal blocks are a common regional anesthetic technique for pediatric surgery involving dermatomes below T10. The technique involves identifying the sacral hiatus using surface anatomy landmarks or ultrasound and inserting a needle to inject local anesthetic with or without adjuvants. Key factors for success include careful identification of anatomy to avoid intravascular or intrathecal injection, use of test dosing to confirm proper placement, and selection of local anesthetics and adjuvants to provide effective pain control. Close monitoring is required after the block due to risks of local anesthetic toxicity, infection, or neurological injury.

































![Bibliography
Baird R, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of caudal blockade versus alternative analgesic strategies for pediatric
inguinal hernia repair. J Ped Surg 2013;48:1077
Cook B, et al. Comparison of adrenaline, clonidine and ketamine on the duration of caudal analgesia produced by bupivacaine in
children. BJA 1995;75:698
Dobereiner E, et al: Evidence-based clinical update: which local anesthetic drug for pediatric caudal block provides optimal
efficacy with the fewest side effects? Can J Anesth 2010;57:1102
Krane E. Spinal epidermoid tumors: will a forgotten complication rise again? [editorial]. Reg Anes Pain Med 1999;24:494
Menzies R, et al. A survey of pediatric caudal extradural anesthesia practice Ped Anesth 2009;19:829
Polaner DM, et al. Pediatric Regional Anesthesia Network (PRAN): a multi-institutional study of the use and incidence of
complications of pediatric regional anesthesia. Anes Analg 2012;115:1353
Roberts S. Ultrasonographic guidance in pediatric regional anesthesia. Part 2: techniques. Pet Anes 2006;16:1112
Tobias J Caudal epidural block: a review of test dosing and recognition of systemic injection in children. Anes Analg
2001;93:1156
Tsui B, et al. Color flow Doppler ultrasonography can distinguish caudal epidural injection from intrathecal injection. Anes Analg
2013;116:1376](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/single-injection-caudal-blocks-for-pediatric-anesthesia-717-240204074259-1d2618a4/85/Single-Injection-Caudal-Blocks-for-Pediatric-Anesthesia-7_17-pptx-37-320.jpg)