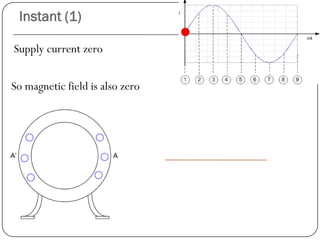
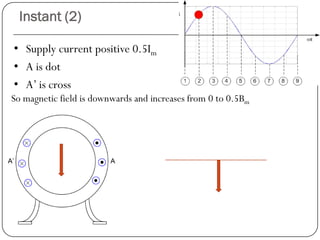
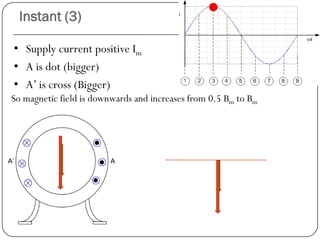
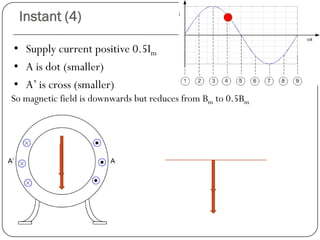
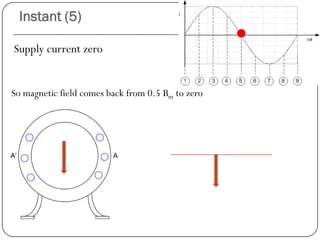
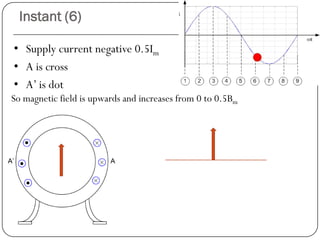
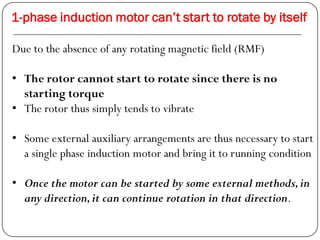
In a single phase induction motor:
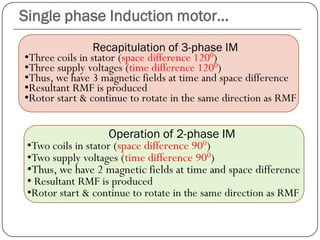
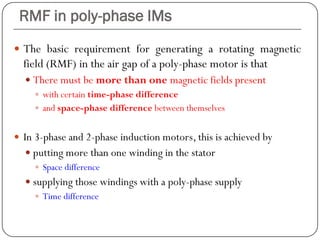
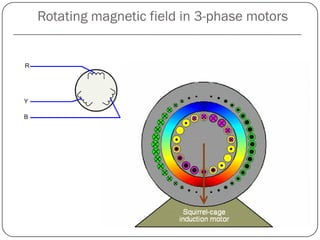
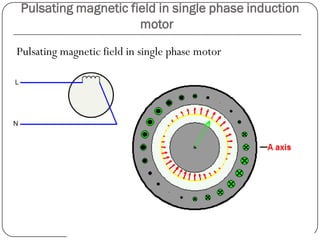
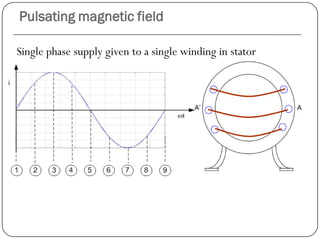
1) The stator generates a pulsating magnetic field rather than a rotating magnetic field, as there is only one winding supplied by a single phase power source.
2) The magnetic field strength varies sinusoidally with time but remains stationary in space.
3) Without additional starting mechanisms, the rotor cannot start rotating due to the lack of a rotating magnetic field and resulting starting torque.