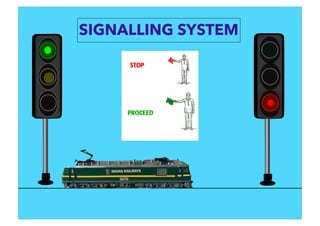
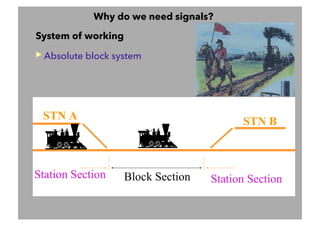
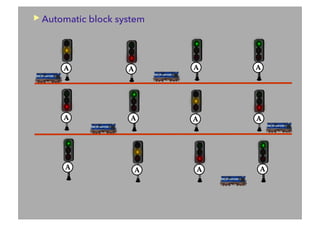
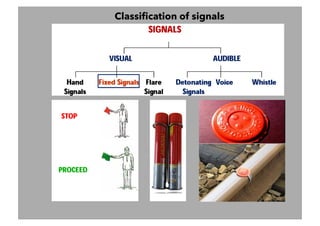
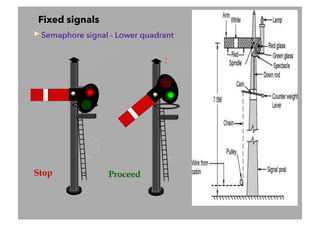
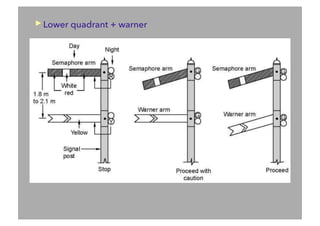
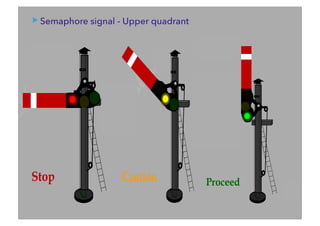
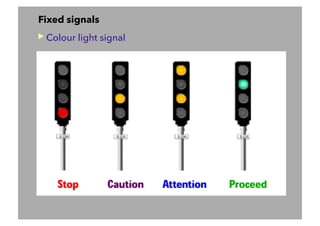
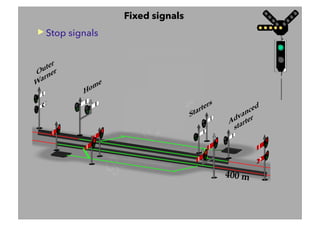
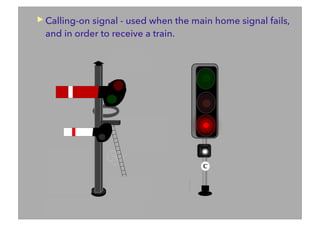
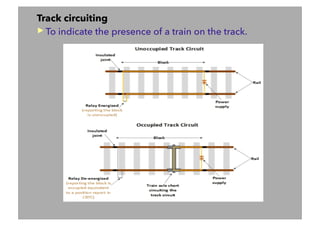
This document discusses railway signalling systems. It begins with an introduction to the author Arun Kumar Sharma and his background and qualifications. It then provides an overview of different types of railway signals including fixed signals like semaphore and colour light signals, as well as subsidiary signals like calling-on and repeater signals. The document notes that signals are needed for the absolute and automatic block systems and explains that the physical appearance of a signal is called its aspect while the information it conveys is called its indication.