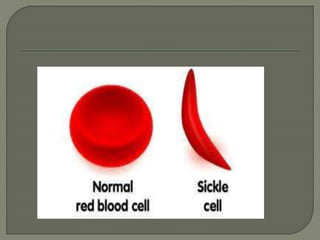
Sickle-cell disease is a group of inherited blood disorders where an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin protein in red blood cells (RBCs) causes them to take on a rigid, sickle shape under certain conditions. This leads to problems like anemia, swelling of hands and feet, and bacterial infections starting around 5-6 months of age. The sickling of RBCs damages their cell membranes over time, decreasing elasticity and causing rigid cells that cannot pass through small blood vessels, leading to vessel blockages and tissue ischemia.