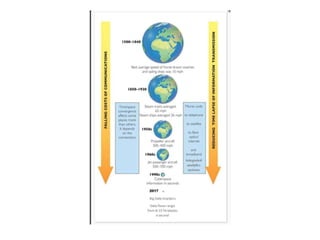
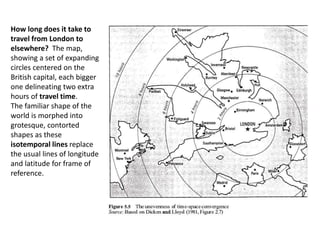
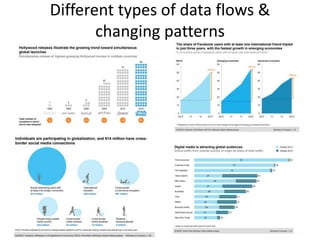
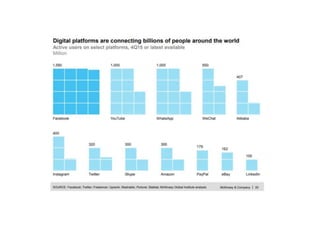
This document discusses time-space compression caused by advances in transportation and communication technology. It defines time-space compression as heightened connectivity that changes perceptions of time, distance, and barriers to movement. Faster travel leads to places feeling closer together than before. Technological changes are driven by both social and economic forces, including the never-ending search for new markets and profits by corporations, and military development of technologies like jets, satellites, and GPS. Global data flow patterns and trends are also changing as a result of these technological innovations.