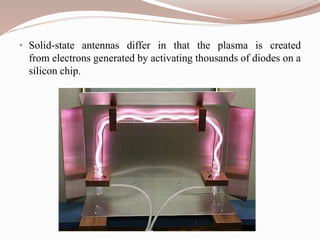
The document discusses plasma antennas, which use ionized gas instead of metal conductors. Plasma antennas have advantages over traditional antennas like higher efficiency and enhanced bandwidth. They operate by ionizing a gas to create plasma that can radiate or receive radio waves. However, plasma antennas also have limitations like higher costs and not being suitable for mobile use. The document reviews the basic principles, operation, characteristics, advantages, limitations and applications of plasma antennas.