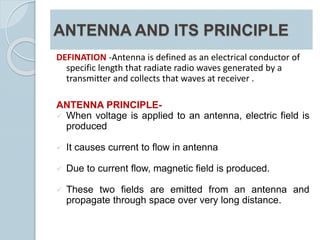
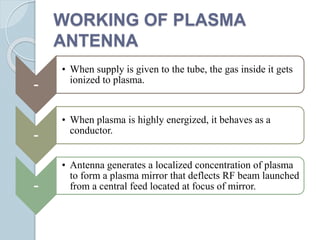
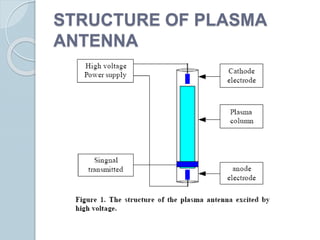
Plasma is the fourth state of matter where a gas is ionized by adding heat or energy. A plasma antenna uses ionized gas enclosed in a tube or enclosure as the conducting element, replacing a solid conductor. When voltage is applied, electric and magnetic fields are emitted that propagate the signal. Plasma antennas have advantages like tunability, invisibility when off, high gain, wide bandwidth, compact size, and short pulse capability making them useful for applications like radar, communications, and stealth technology.