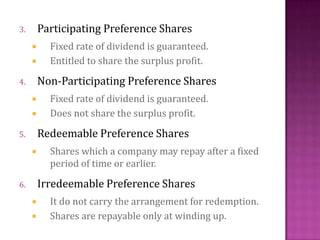
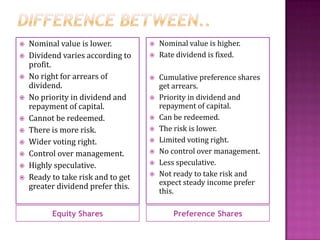
This document discusses different types of company shares. It defines a share and notes there are two main classes: preference shares and equity shares. Preference shares offer a fixed dividend rate and right to capital repayment before equity shares. Equity shares have voting rights but no fixed dividend. The document outlines various types of preference shares, including cumulative, participating, redeemable, and convertible varieties. It also describes employee shares and compares key characteristics of preference versus equity shares.