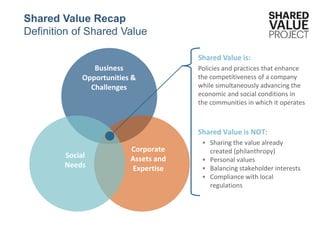
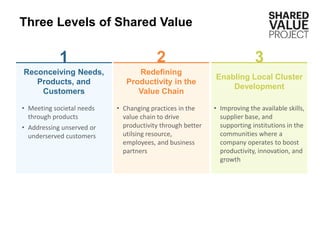
The document discusses the concept of 'shared value' as a paradigm that links corporate success to societal improvement, emphasizing that businesses can create economic value by addressing social issues. It distinguishes shared value from traditional corporate philanthropy and social responsibility by highlighting its focus on new business opportunities derived from social problems. Examples showcase how companies like Arauco and Yara successfully integrate shared value into their operations to enhance both community welfare and their profitability.