This document discusses bending moment and shear force for beams. It contains 3 main sections:
1) An introduction to bending moment, shear force, and the relationship between loading, shear force and bending moment.
2) How to draw shear force diagrams and bending moment diagrams by calculating shear forces and bending moments at critical points along a beam.
3) How to calculate reactions for simply supported beams and cantilever beams by applying equations of equilibrium. Several examples of calculating reactions are provided.
![BENDING
MOMENT AND
SHEAR FORCE
[16 MARKS]
Chapter 2
Chapter Details
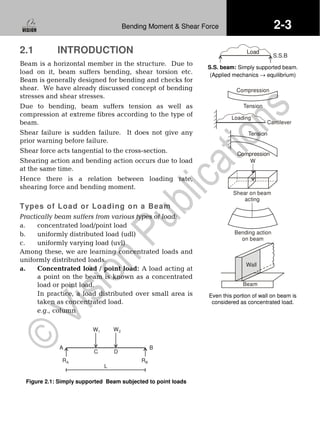
2.1 Introduction
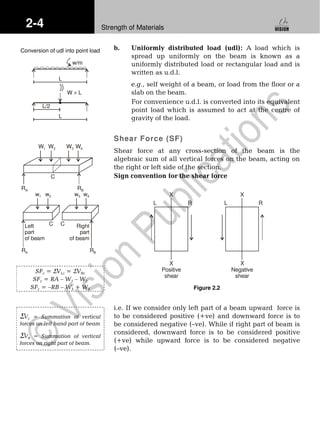
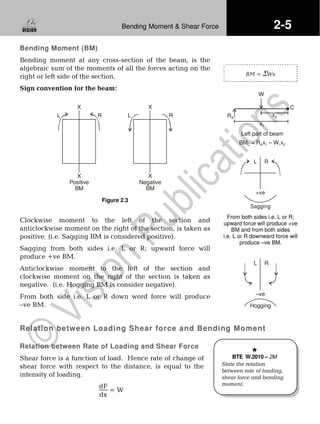
2.2 Shear Force Diagram (SFD) and
Bending Moment Diagram (BMD)
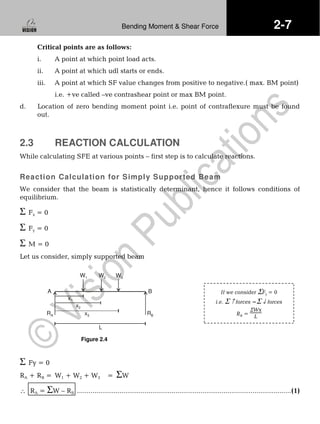
2.3 Reaction Calculation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfandbm-141229233111-conversion-gate02/75/Sf-and-bm-1-2048.jpg)