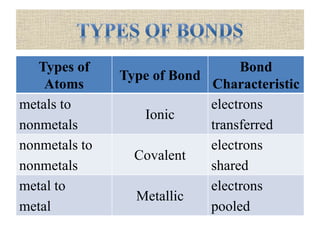
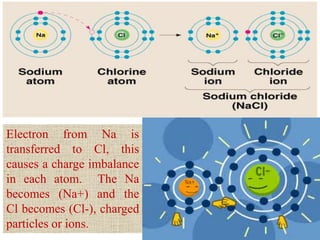
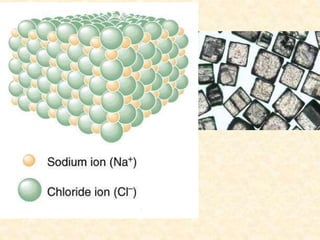
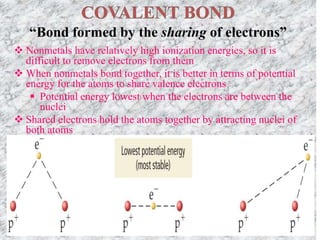
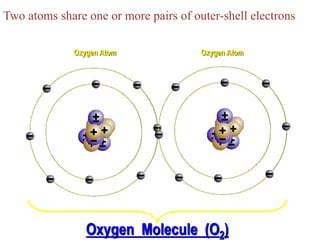
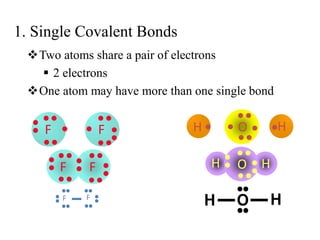
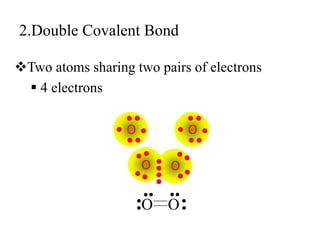
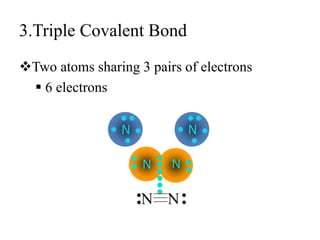
This document discusses different types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals when electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the nonmetal atom. Covalent bonds form between nonmetal atoms through the sharing of electron pairs. Metallic bonds form between metal atoms when electrons are delocalized and pooled throughout the structure. Examples of ionic bonding forming between sodium and chlorine atoms and covalent bonding forming between oxygen and hydrogen atoms are provided. Single, double, and triple covalent bonds are also defined based on the number of electron pairs shared.