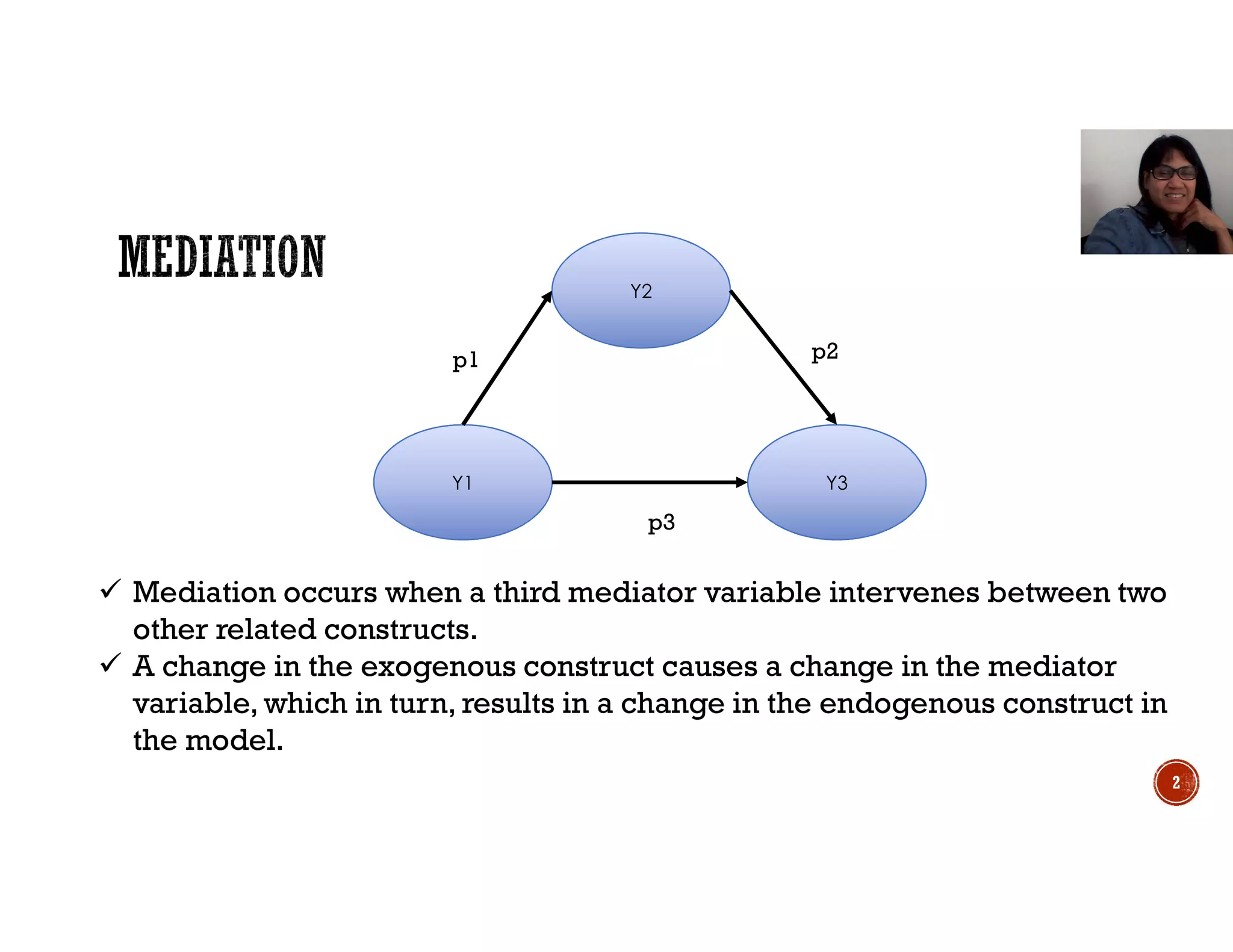
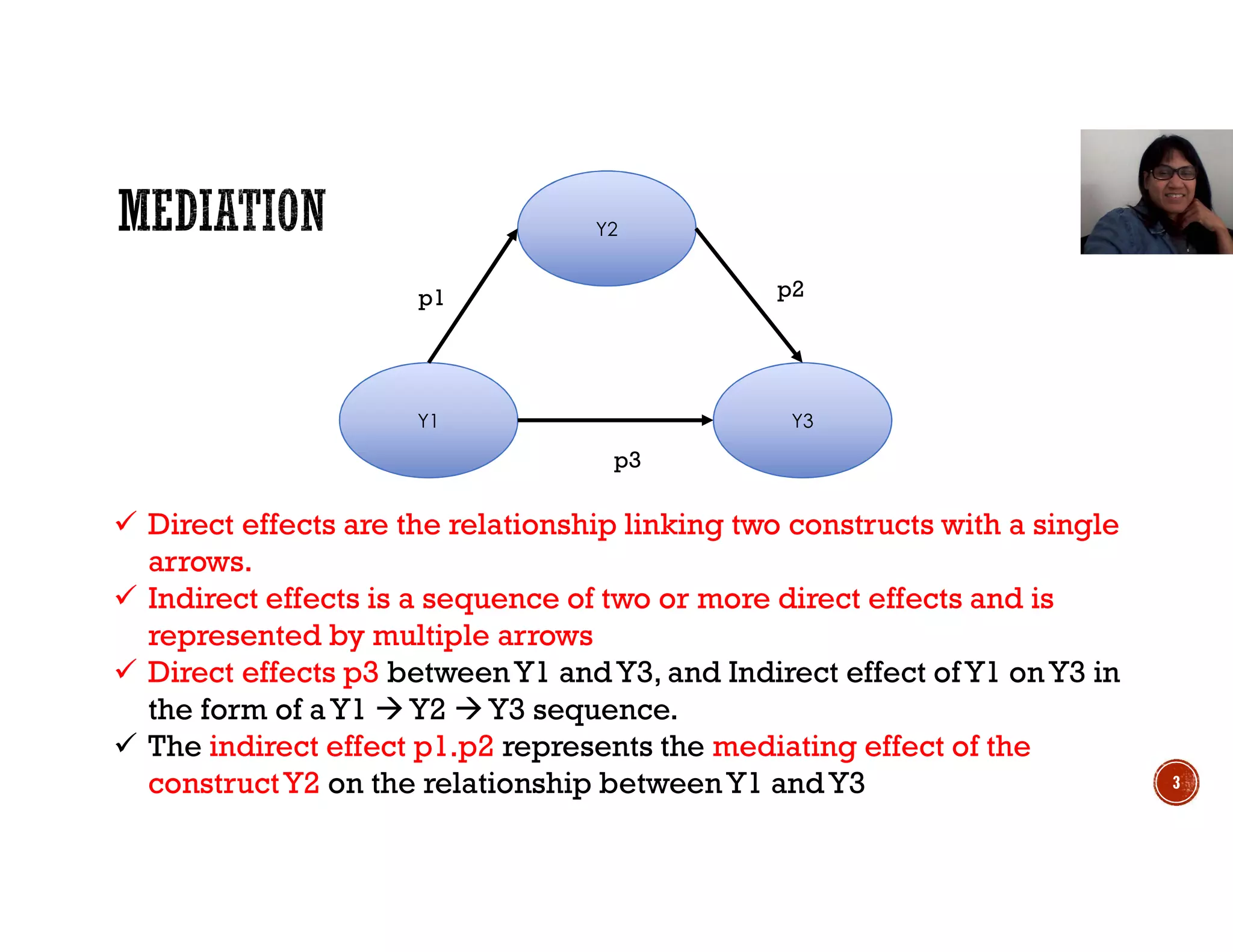
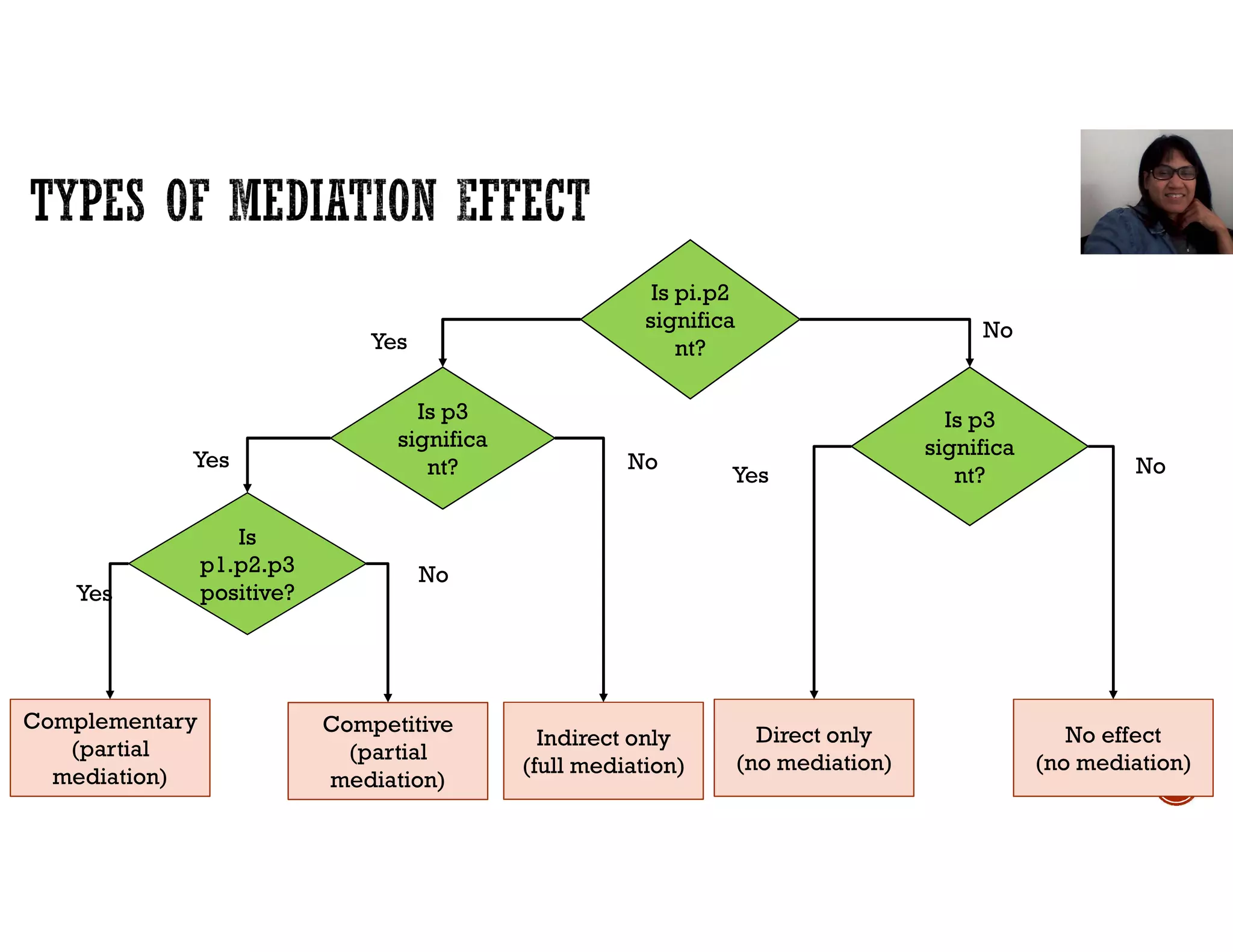
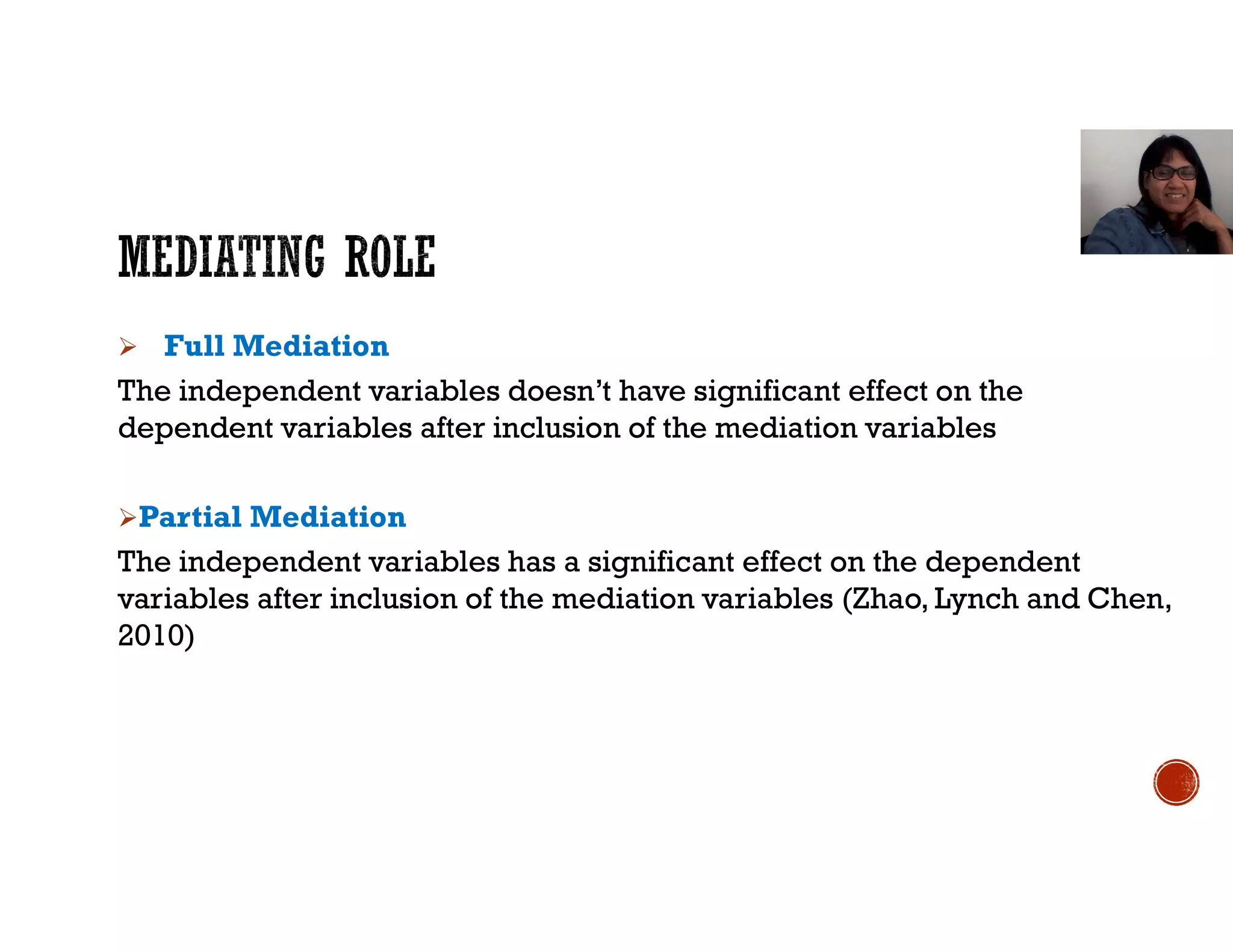
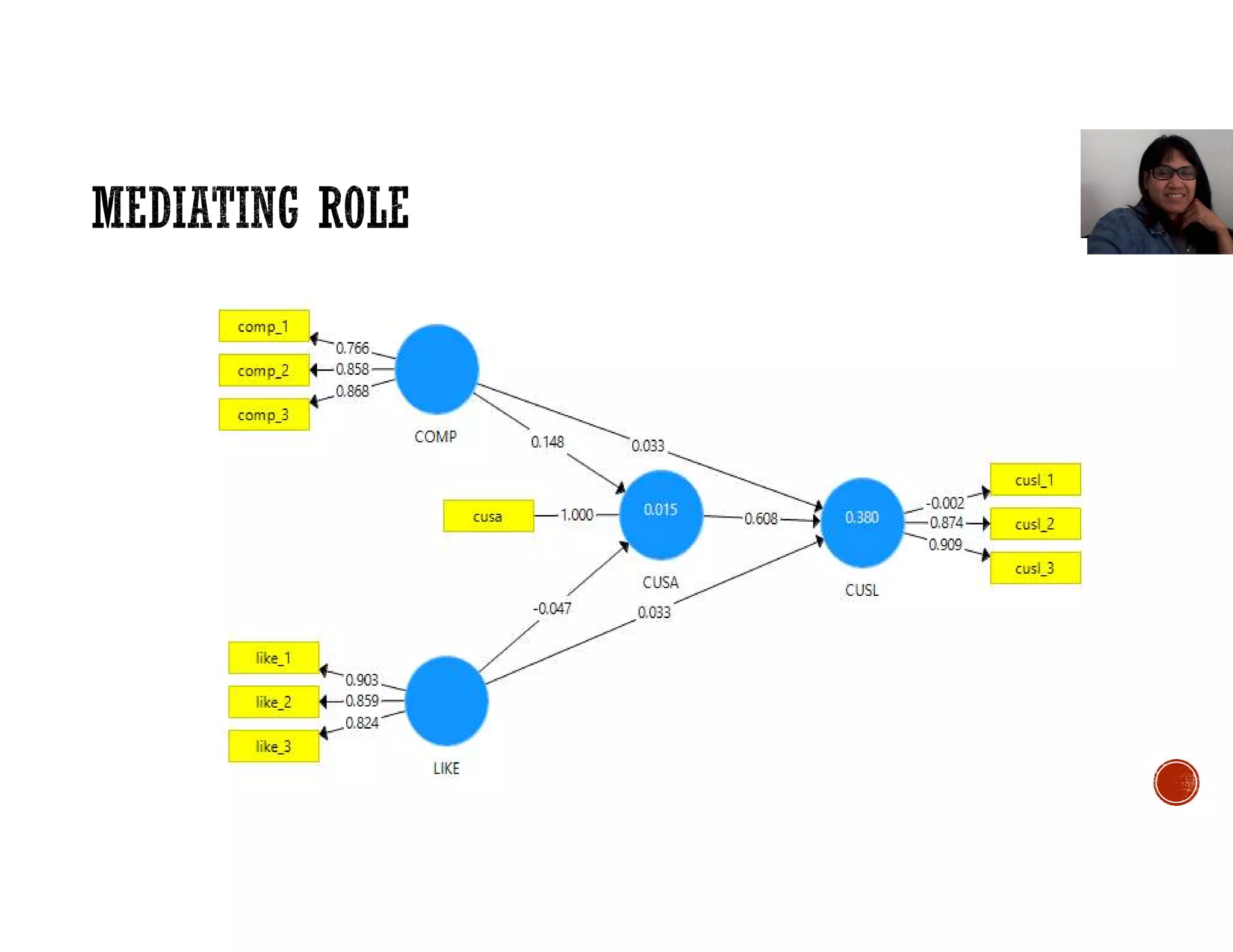
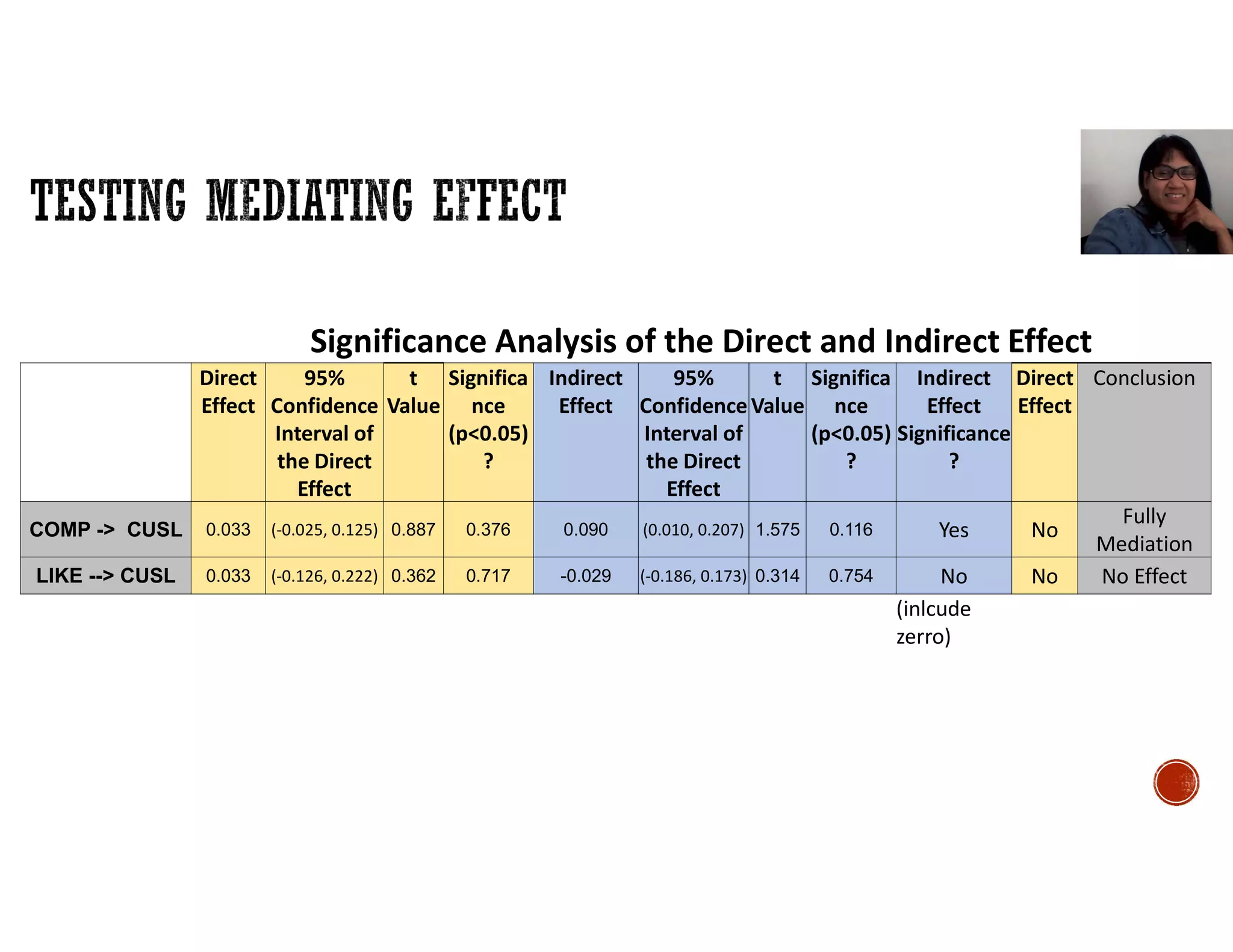
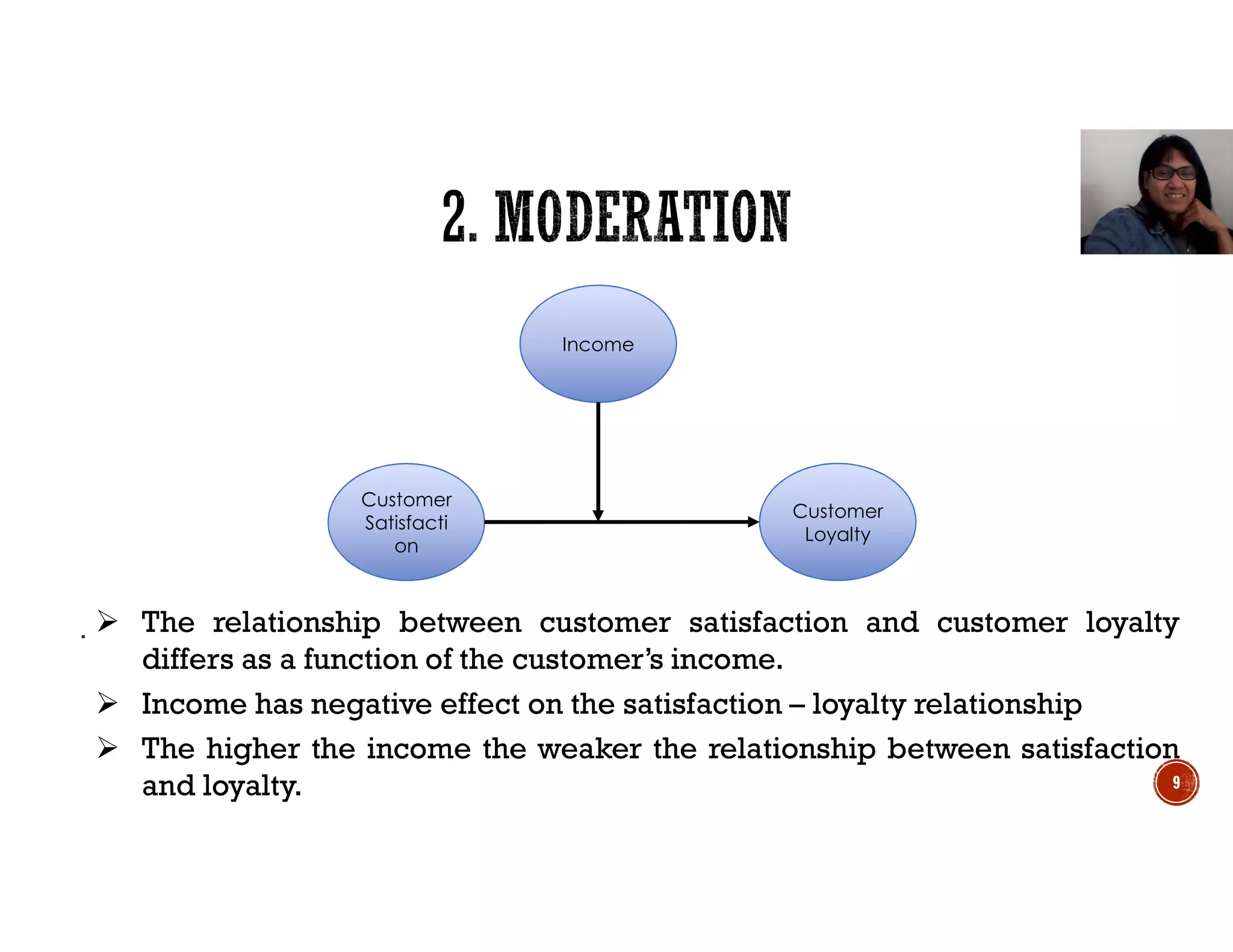
This document discusses mediation, moderation, and how to analyze them in structural equation modeling. It defines mediation as occurring when a third variable intervenes between two related constructs, so that a change in one construct causes a change in the mediator variable, which then causes a change in the other construct. It also defines direct and indirect effects. It discusses how to determine if an effect is fully or partially mediated. It then defines moderation as a situation where the relationship between two constructs depends on a third variable, and discusses how to model and test for a moderating effect.