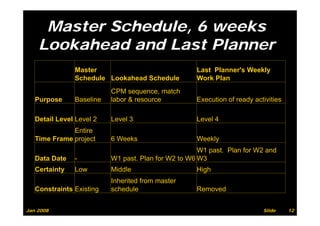
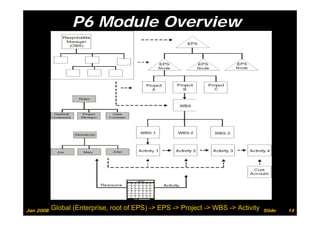
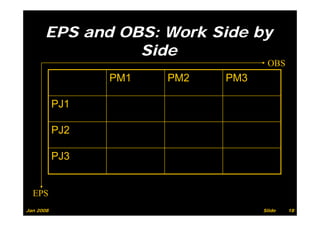
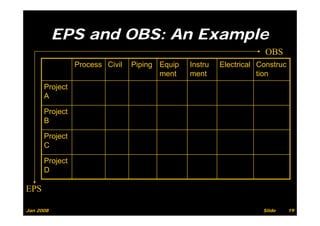
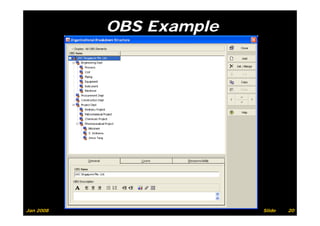
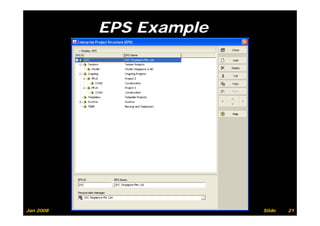
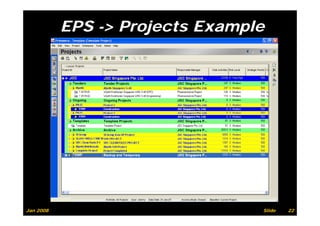
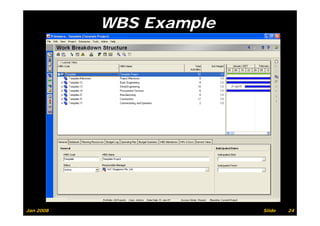
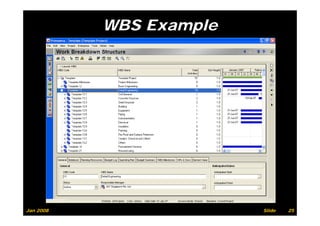
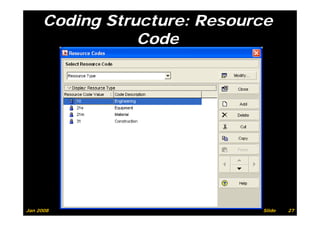
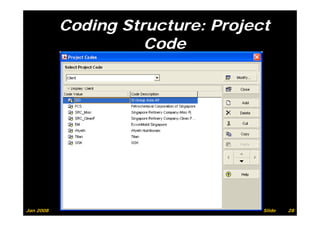
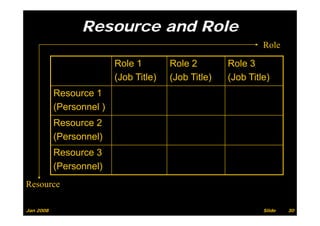
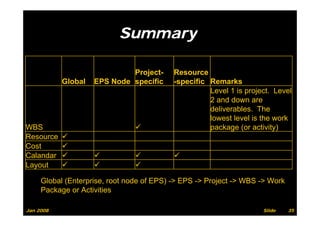
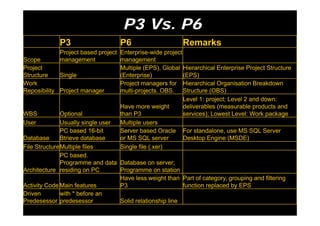
The document provides information on planning and scheduling basics in project management, including defining a project, characteristics of a project, defining activities, setting up a project in Primavera P6, monitoring project progress, and performance measurement using earned value analysis. It also discusses lean construction concepts, and compares Primavera P3 and P6 project management software.