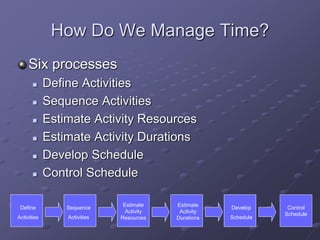
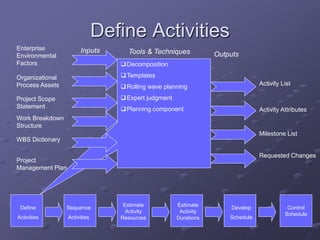
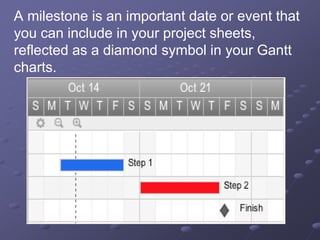
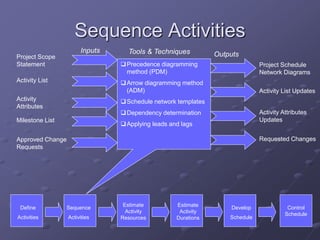
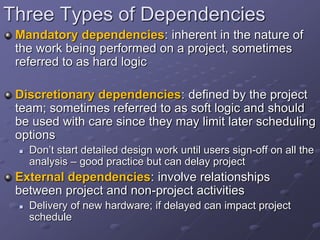
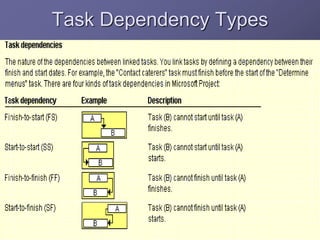
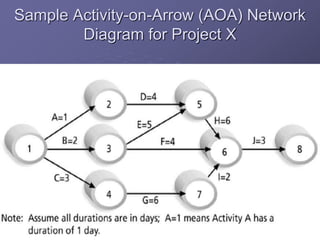
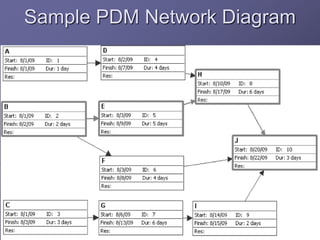
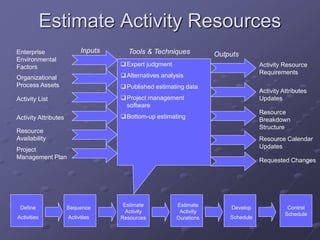
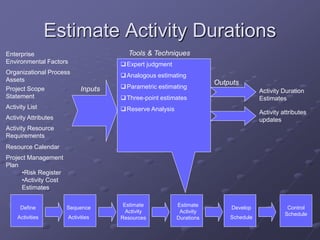
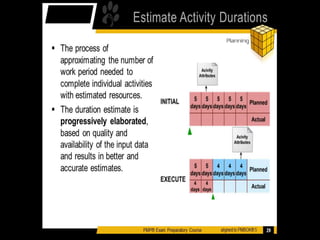
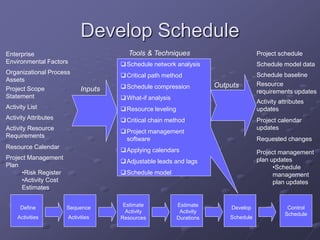
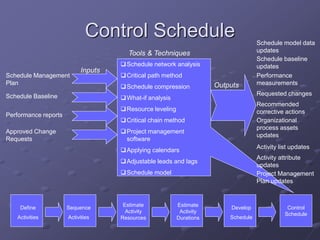
The document discusses project time management and the six key processes involved: define activities, sequence activities, estimate activity resources, estimate activity durations, develop schedule, and control schedule. It provides details on each process, including defining activities and their attributes, determining dependencies between activities, estimating resource needs and durations, developing a schedule using techniques like critical path method, and controlling the project schedule.