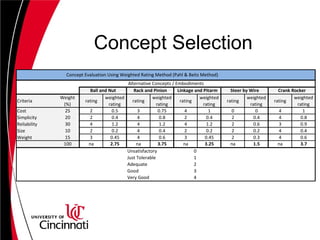
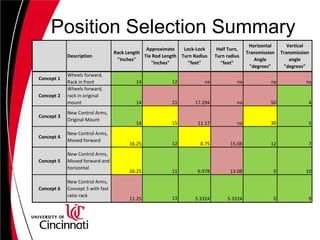
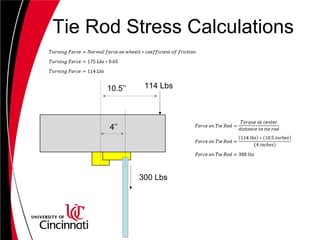
The document describes the design of a steering system for a Baja vehicle. It discusses several concept designs and evaluates them based on criteria like cost, simplicity, reliability, weight, and size. Concepts considered include rack and pinion, linkage systems, and steer-by-wire. Analysis and calculations are shown for rack location, tie rod design, and component selection. The double crank rocker linkage concept is selected as the final design due to its simplicity, low cost and weight. Detailed specifications are provided for tie rods, steering shaft, and other components.