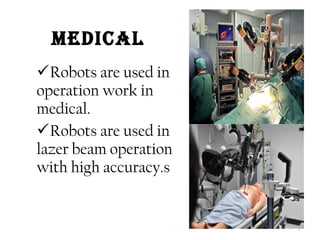
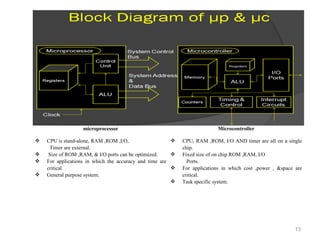
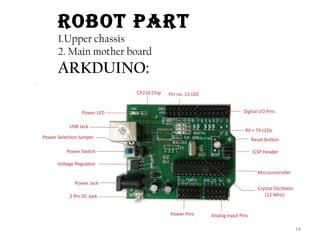
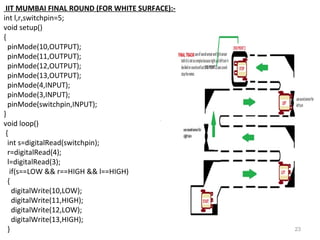
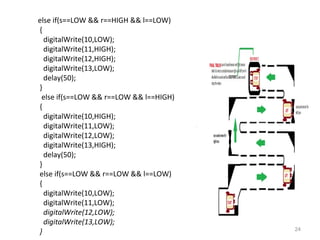
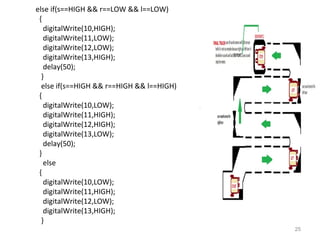
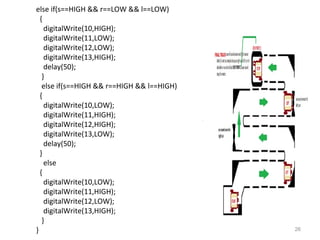
This document summarizes a seminar report on robotics. It defines a robot as an electromechanical device that can perform tasks automatically or by remote control. Robots are used in various industries like automotive, manufacturing, medical, military, space exploration, and research. The document discusses the applications of robots in these industries. It also explains the need for robots and identifies their main components as sensors, processors, actuators and motors that work together to give robots movement and ability to interact with their surroundings. The document provides examples of different sensors, motors and a sample Arduino code for robot movement.