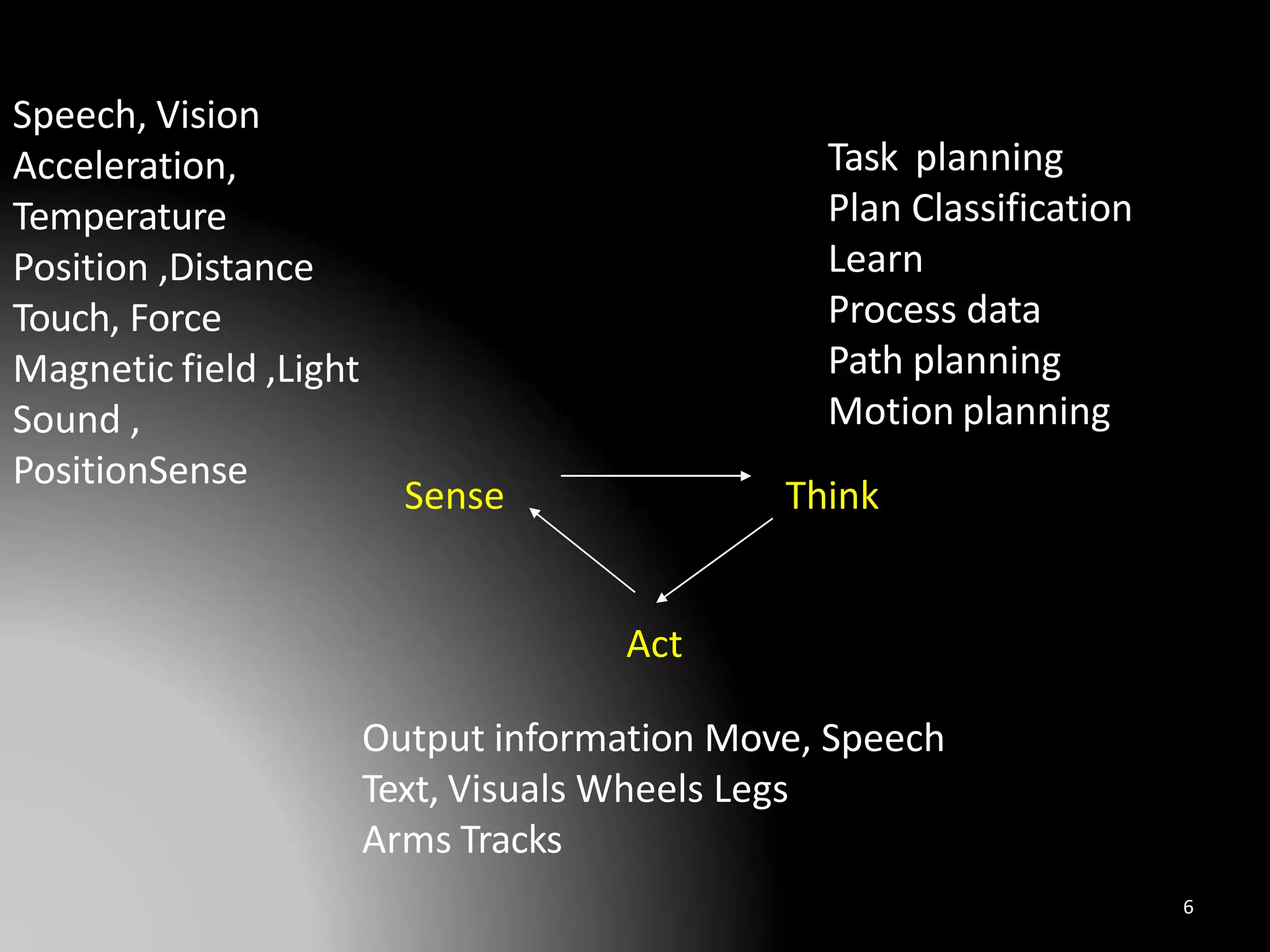
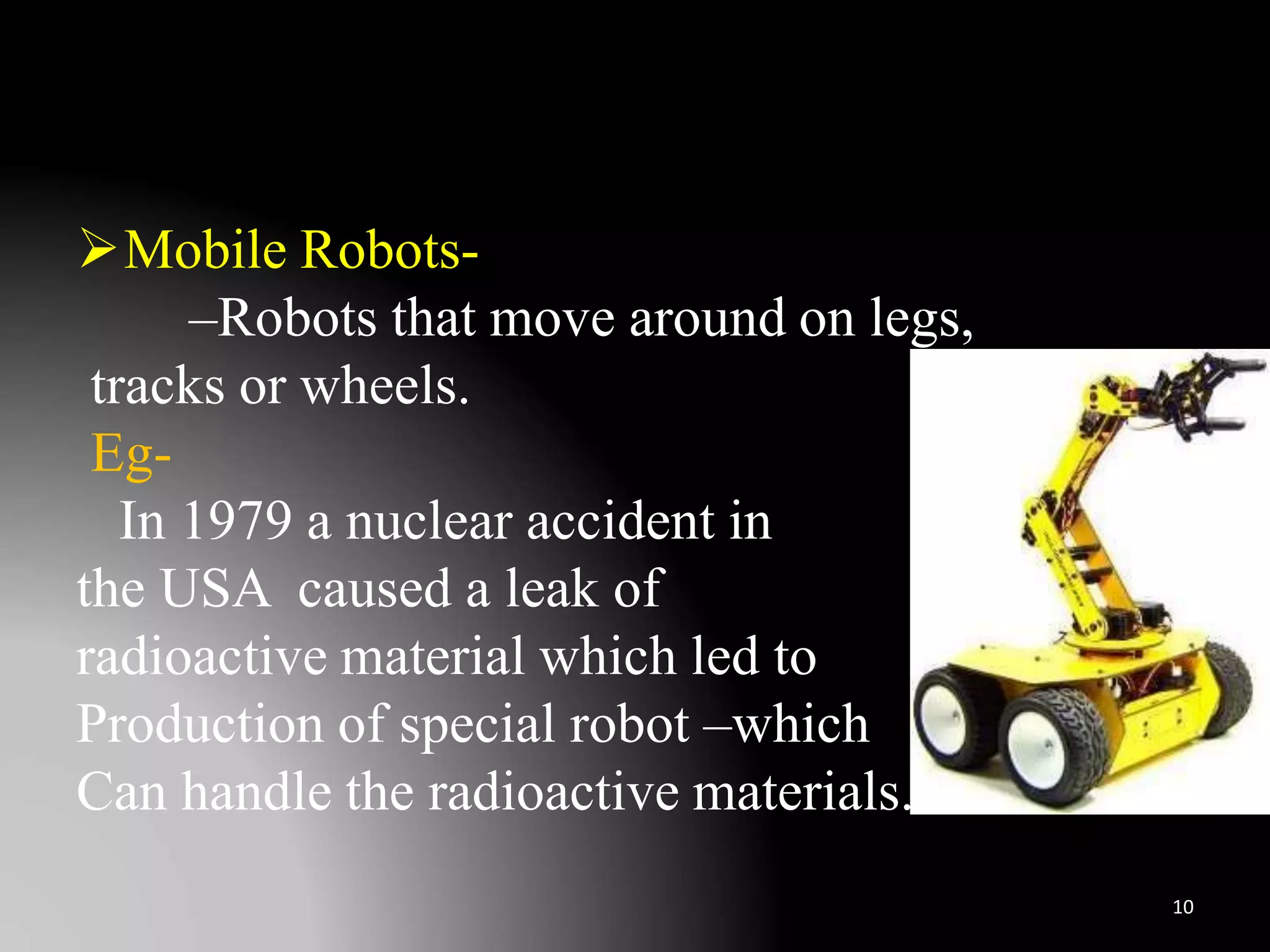
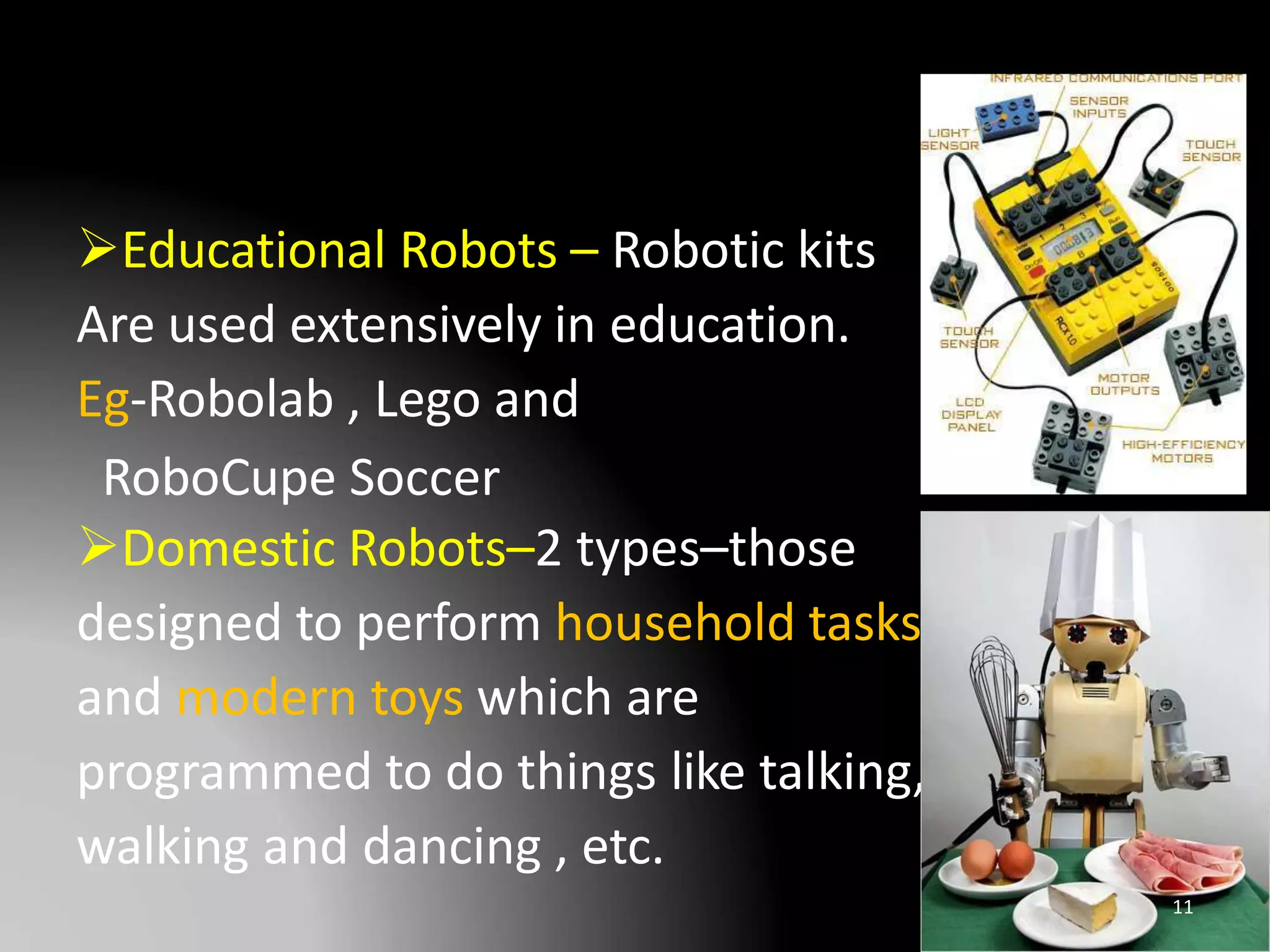
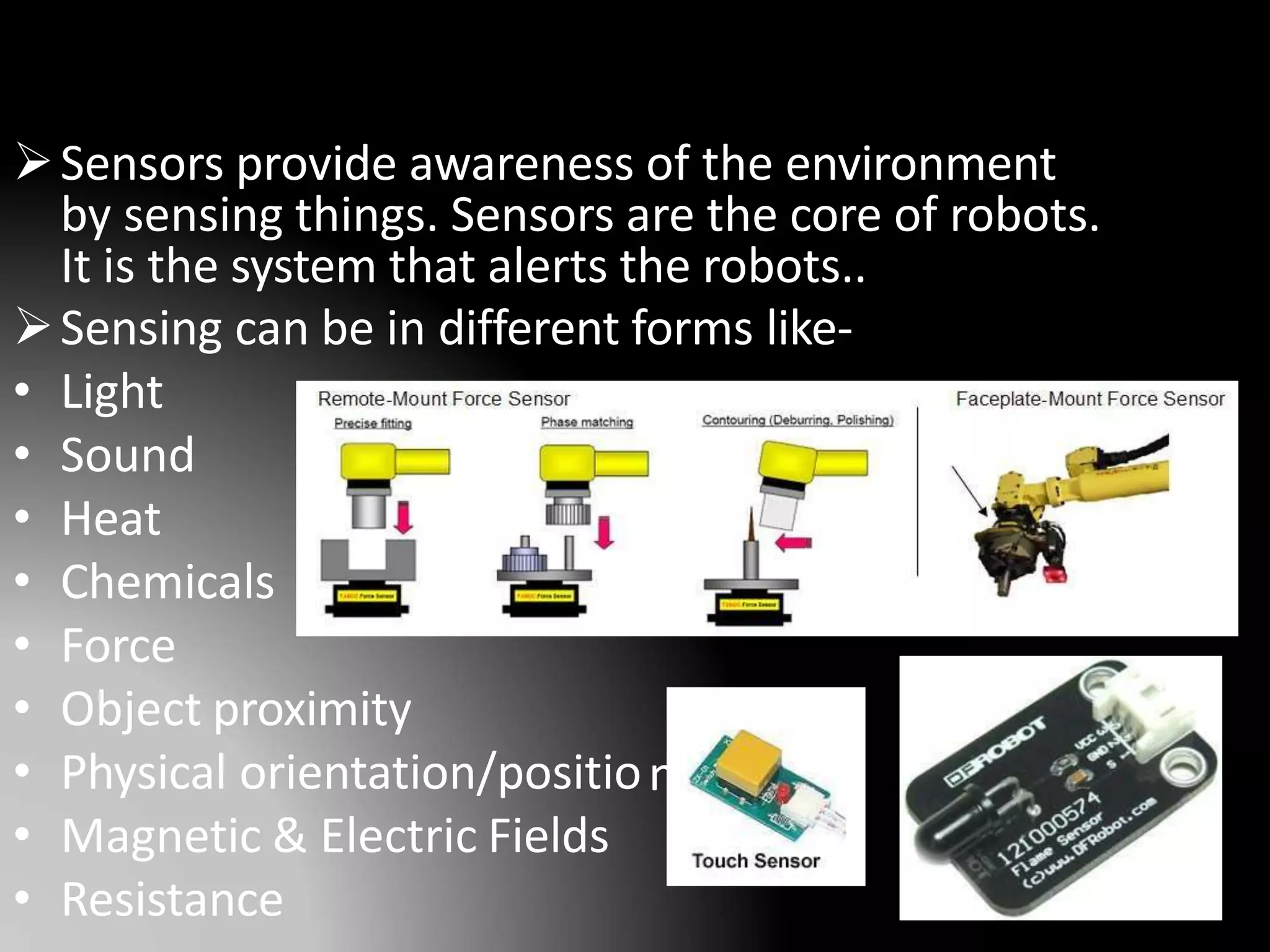
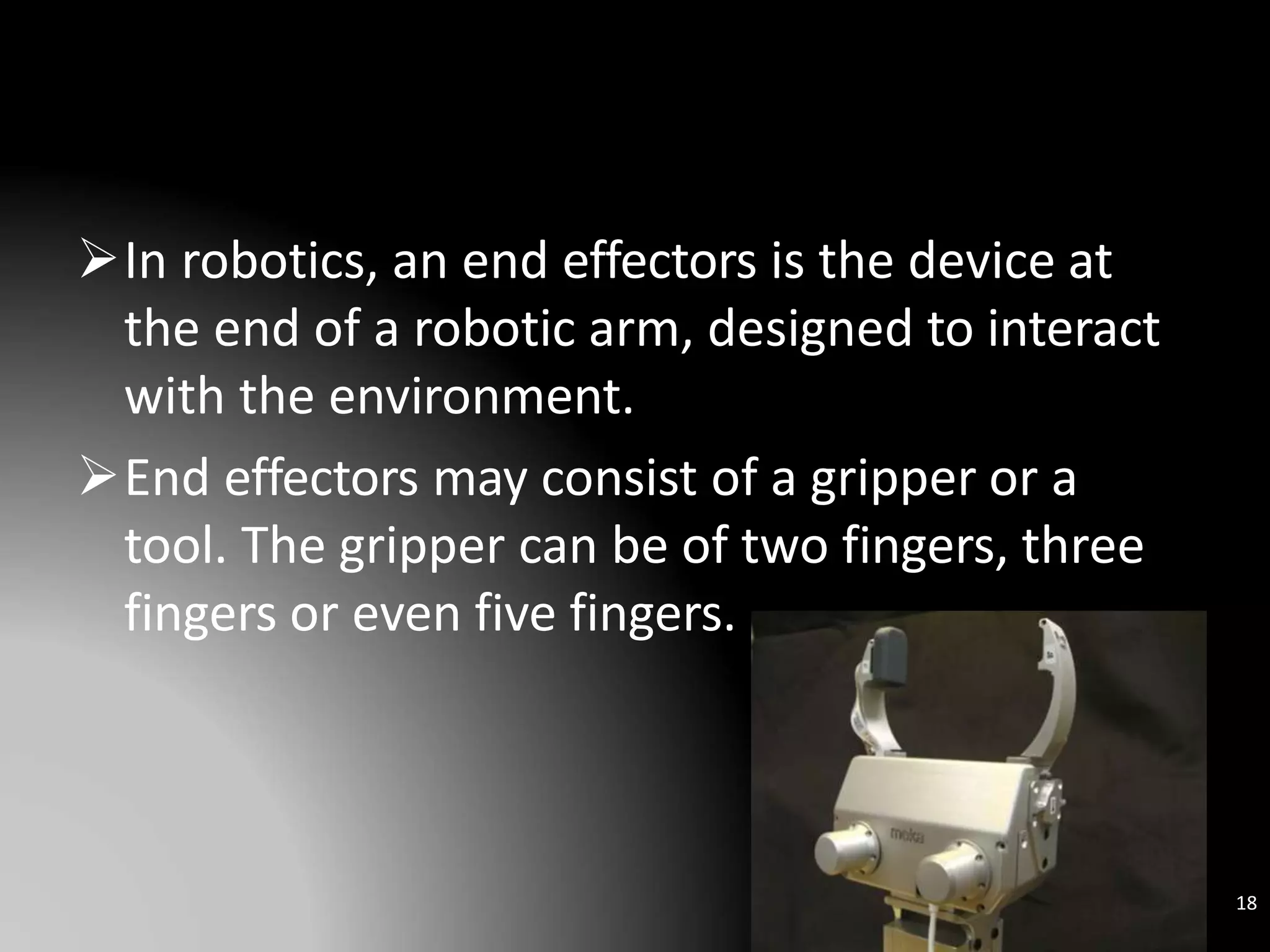
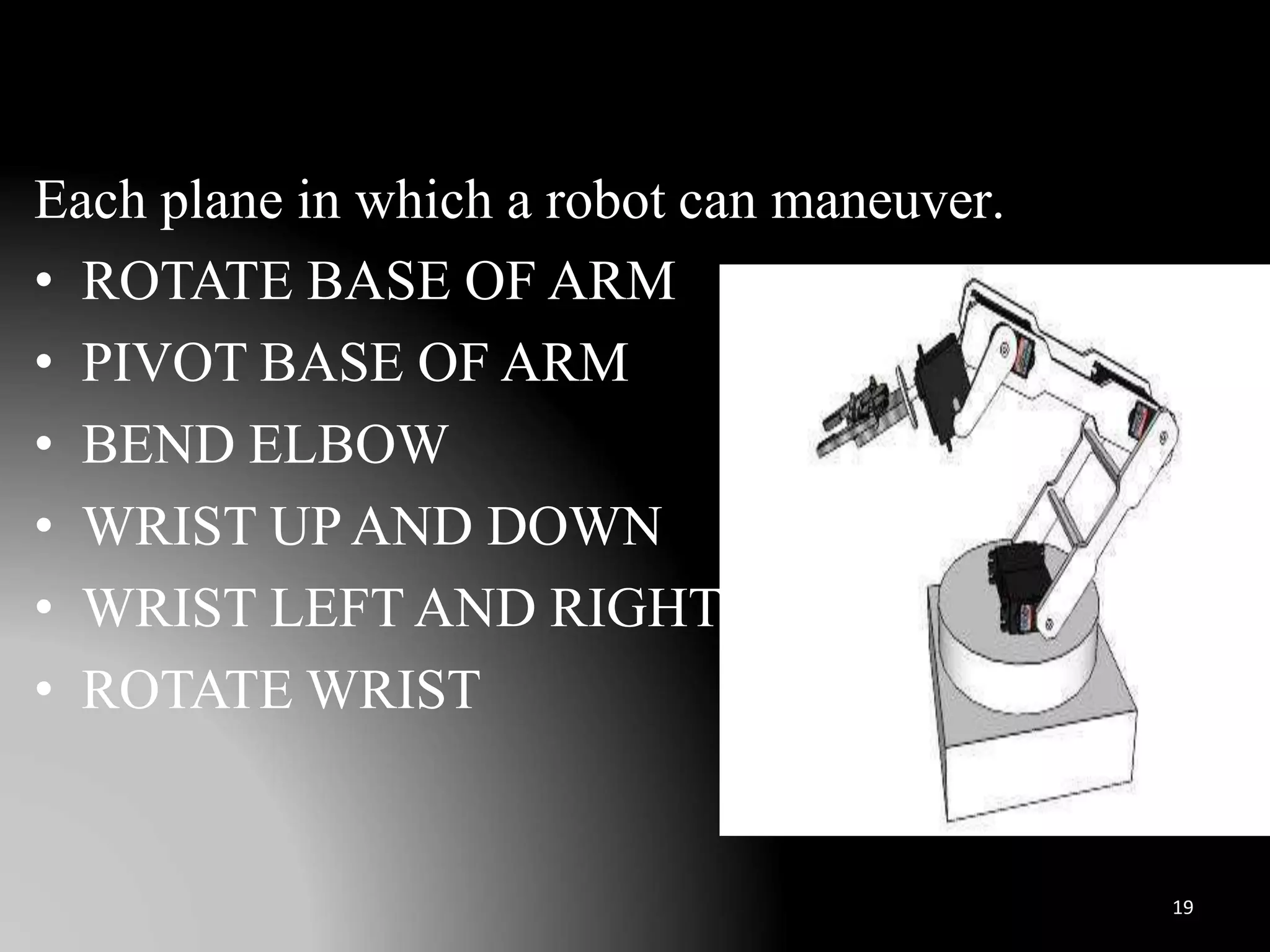
The document discusses the history and definitions of robots. It begins by explaining that the term "robot" was first coined in 1920 in a play and comes from the Czech word for forced labor. It then provides definitions for robot, robotics, and telerobotics. The document also summarizes Isaac Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics and discusses the key components and functions of robots including sensing, locomotion, manipulation, end effectors, and degrees of freedom. It concludes by outlining applications of robots in exploration, medical science, assembly, and other fields.