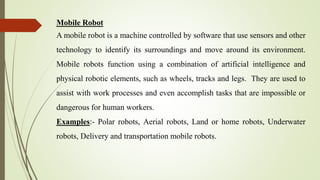
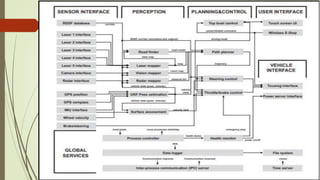
The document provides an overview of robotics, including the key topics of: building blocks of robots such as actuators, sensors, processors and controllers; classifications of robots into manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoids; functions involved in robotic movement; software architectures; applications of AI in robotics; application domains; and pros and cons of robots. It introduces robotics and defines a robot, then discusses each topic in 1-2 paragraphs with examples.