This document discusses semantics, the study of meaning in language. It defines semantics as understanding the meaning of words, morphemes, phrases and sentences. It also discusses three types of semantic analysis: semantic features which describe the components of a word's meaning using properties and values, semantic roles which describe the roles that entities play in sentences, such as agent, theme, or experiencer, and lexical relations which describe relationships between words. Examples are provided to illustrate semantic features and roles. The document is about defining semantics and the different approaches used in semantic analysis.





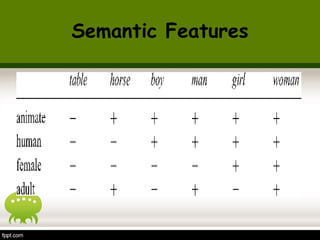
![• Semantic properties: The components of
meaning of a word.
• Meaning as collection of
properties/features typically with two
possible values (+ / -)
• Example of componential analysis:
baby is [+ young], [+ human], [+animate]
Semantic Features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticspresentation-130718011030-phpapp01/85/Semantics-6-320.jpg)
![Identify the features (1)
1.(a) widow, mother, sister, aunt, maid
(b) widower, father, brother, uncle
The (a) and (b) words are
The (a) words are
The (b) words are
2. (a) bachelor, paperboy, pope, chief
(b) bull, rooster, drake, ram
The (a) and (b) words are
The (a) words are
The (b) words are
[+ human]
[+ female]
[+ male]
[+ male]
[+ human]
[+ animal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticspresentation-130718011030-phpapp01/85/Semantics-8-320.jpg)


