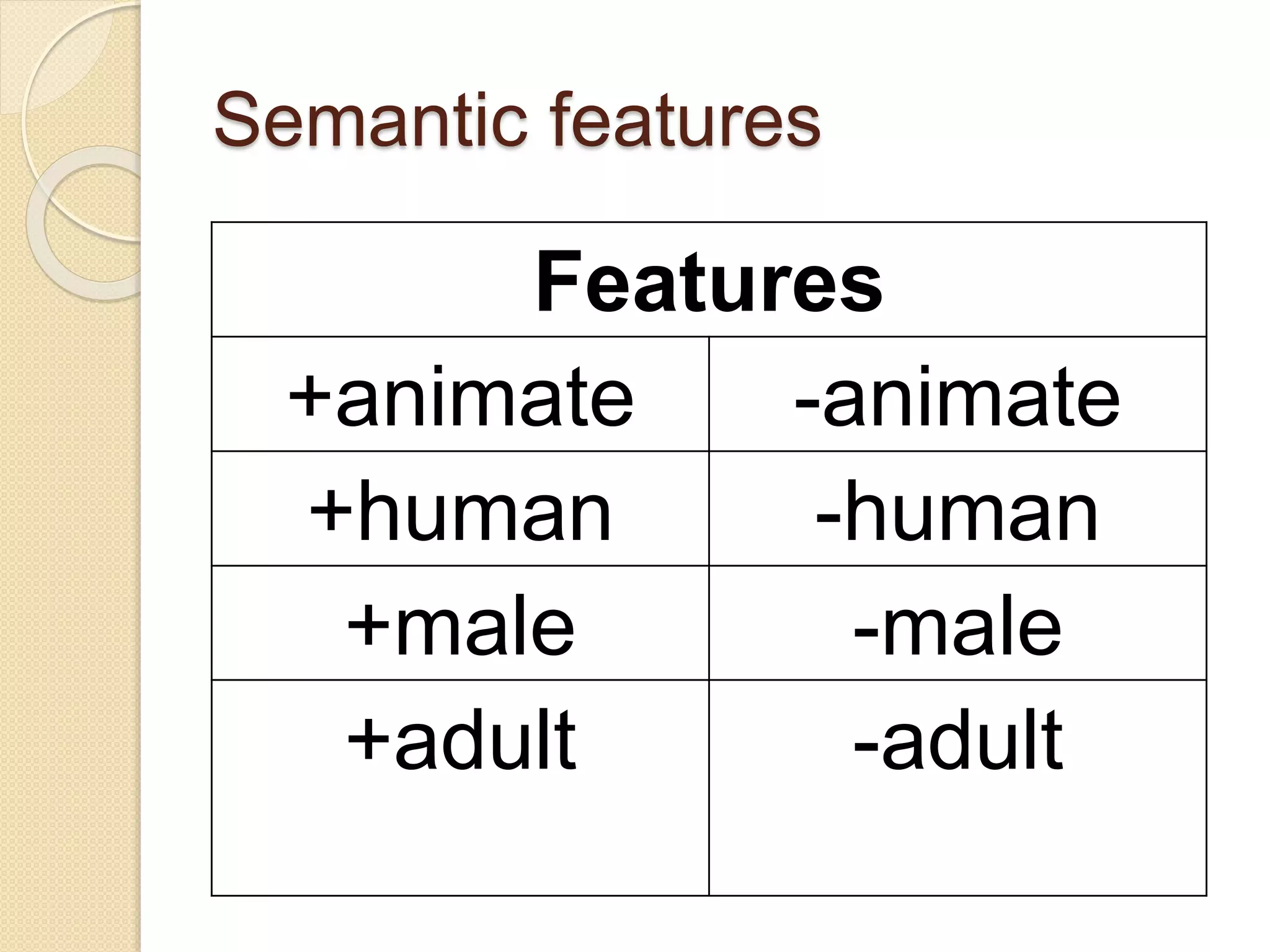
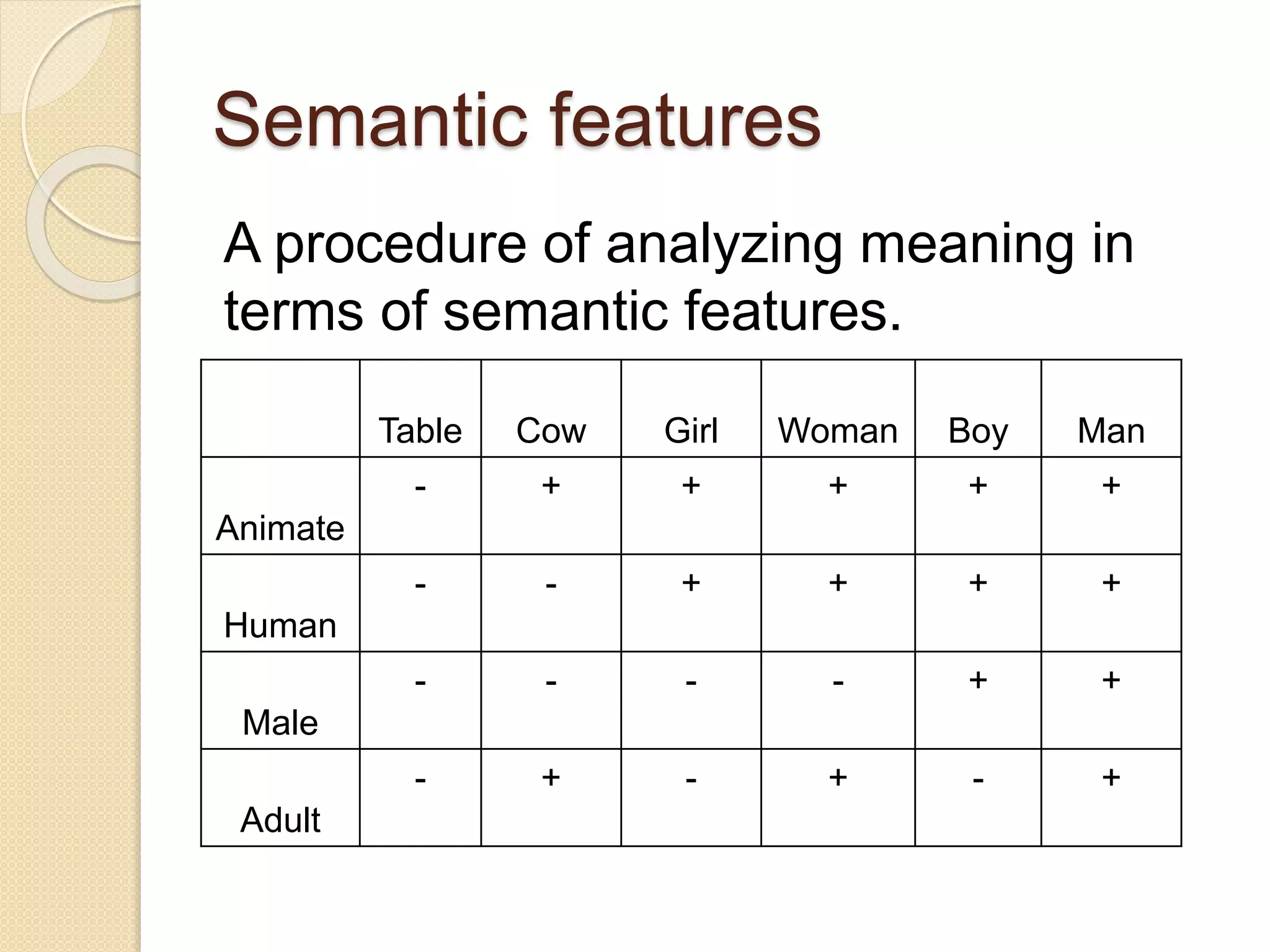
This document defines semantics and discusses its key concepts. Semantics is the study of meaning in language. It has two types of meaning: conceptual meaning, which is the basic literal definition, and associative meaning, which involves connotations. Words can be analyzed using semantic features like animate vs inanimate. Semantic roles examine the relationships between words in a sentence, such as agent, theme, and instrument. Semantics plays an important role in understanding language.