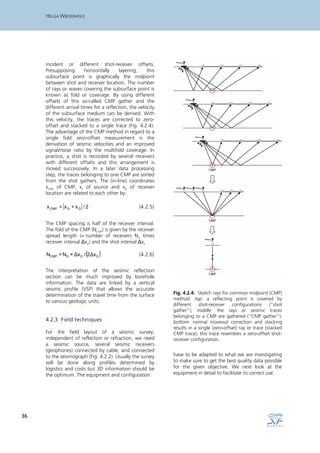
Seismic methods use seismic waves created by impacts on the surface to map underground structures. The waves travel through underground layers and are reflected or refracted at boundaries between different materials. Analysis of the travel times and velocities of the waves allows determining the depth and type of geological layers. Seismic reflection techniques involve creating waves at shot points and recording them with receivers at different offsets to generate common midpoint gathers. Processing the gathers yields a seismic section that images layer boundaries like an echo sounder. Seismic refraction uses refracted head waves along interfaces to build a shallow velocity model for near-surface layers. Both methods together provide structural and physical characterization of underground features like buried valleys.